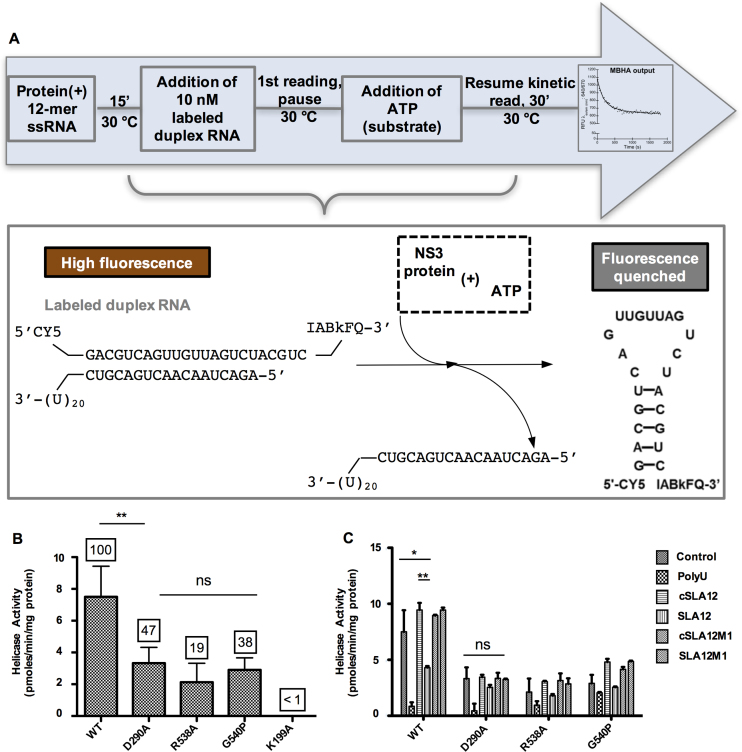
Figure 5.
Helicase activity of WT or mutant NS3 proteins determined by the MBHA. (A) Schematic depiction of MBHA. Duplex RNA used in the assay contains one strand labeled with a cyanine 5 (Cy5) fluorophore at the 5′ end and an Iowa Black FQ (IABkFQ) quencher at the 3′ end. A complementary strand has a U20 overhang for the loading/recruitment of the helicase. ATP-dependent unwinding results in the release of the fluorophore/quencher labeled RNA that forms a hairpin to quench the fluorescence emitted by the fluorophore. (B) Specific activity of NS3 mutant proteins as compared to WT protein. The numbers on top of the bars represent percentage of helicase activity based on WT NS3 which is denoted as 100%. (C) Competition of 12-mer RNA with duplex RNA in the helicase assay as measured for WT, D290A, R538A and G540P proteins. In order to understand the interplay between duplex RNA and ATP binding, we investigated the impact of adding the various 12-mer RNAs or polyU to the MBHA mixture for measuring unwinding activity of the WT and mutant NS3 proteins. A control reaction without any 12-mer RNA was included to compare the activity level. In order to understand the interplay between duplex RNA and ATP binding, we investigated the impact of adding the various 12-mer RNAs or polyU to the MBHA mixture for measuring unwinding activity of the WT and mutant proteins. Error bars represent the standard error of mean of duplicate measurements and significant differences are shown by the bars within the plots with asterisks (*P ≤ 0.10, **P ≤ 0.05 and ns = no significant difference).