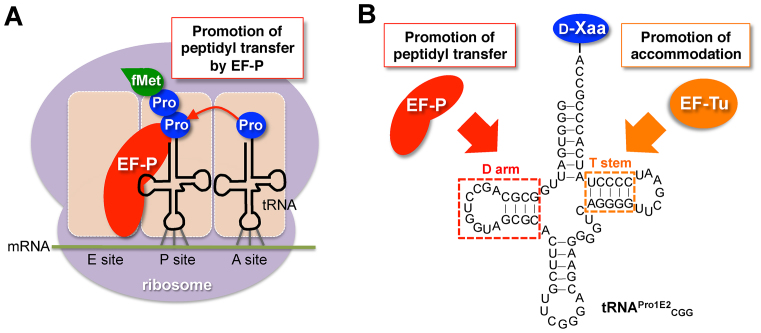
Figure 1.
Schematic depiction of promotion of proline and d-amino acid incorporation mediated by EF-P. (A) Role of EF-P in acceleration of consecutive proline incorporation. EF-P binds to ribosome in between E site and P site, and interact with the P-site peptidyl-prolyl-tRNA to accelerate peptidyl transfer between the P-site peptidyl-prolyl-tRNA and the A-site prolyl-tRNA. (B) Construct of d-aminoacyl-tRNA with optimized D-arm and T-stem structures. A specific D-arm structure consisting of 9-nt D-loop closed by a stable D-stem sequence recruits EF-P on to the tRNA and promotes peptidyl transfer between d-amino acids. A specific T-stem structure improves EF-Tu-binding affinity and accommodation rate of the d-aminoacyl-tRNA on to the ribosomal A site.