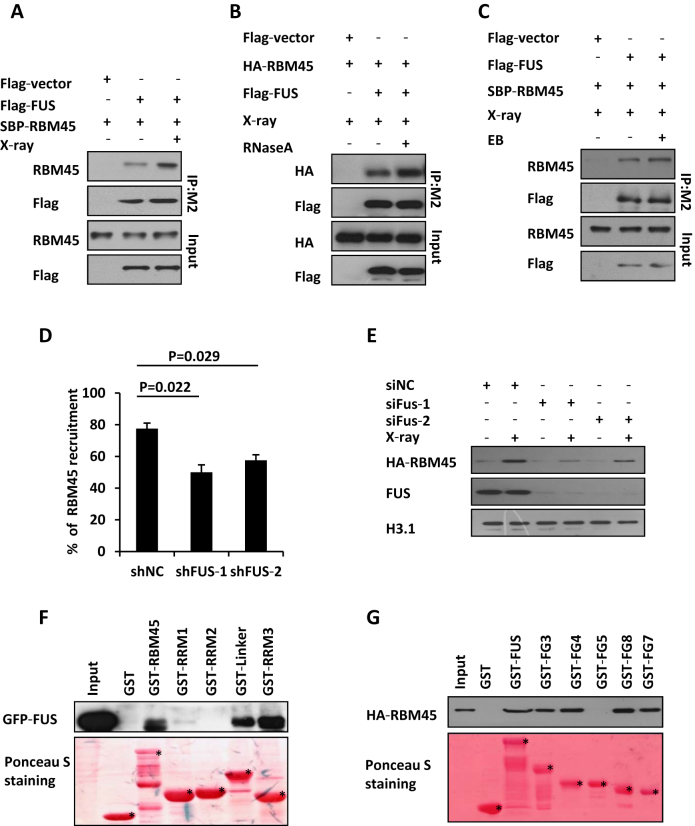
Figure 5.
RBM45 interacts with FUS which promotes its recruitment. (A) Detection the interaction of RBM45 and FUS by Immunoprecipitation. 293T cells co-transfected with Flag-FUS and SBP-RBM45 were lysed immediately upon 10 Gy of X-ray exposure. Anti-M2 Flag beads were used for immunoprecipitation. The Immunoprecipitates (IP) and inputs were immunoblotted with antibodies against RBM45 or flag, respectively. (B) RNA is not essential for the interaction between RBM45 and FUS. 293T cells co-transfected with Flag-FUS and HA-RBM45 were lysed immediately upon 10 Gy of X-ray exposure. 100 μl RNase A (1 mg/ml) or PBS was added to 900 μl 293T lysate before immunoprecipitation with M2 beads. Antibodies against HA or Flag were used for immunoblotting. (C) DNA is not essential for the interaction between RBM45 and FUS. 293T cells were treated as in (A). The lysates were supplemented with or without EB (200 μg/ml) prior to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag M2 beads. (D) FUS promotes the recruitment of RBM45 to DNA damage sites. 48 h after expressing the indicated mCherry-shRNA, U2OS cells were transfected with GFP-RBM45. Then cells were micro-irradiated. NC: negative control. Data are presented as mean ± SD. n = 2; 30–40 irradiated cells per experiment. P values from unpaired t test were included. (E) Immunoblotting the chromatin fractions from cells expressing siNC or siFUS to examine the enrichment of HA-RBM45 on chromatin after DNA damage. (F) Mapping the functional domains of RBM45 that interact with FUS by GST pull down assay. Purified GST-RBM45 fragments were incubated with the lysates of 293T cells expressing GFP-FUS followed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody. GST-fusion proteins were shown by Ponceau S staining of the PVDF membrane. Asterisks mean specific bands. (G) GST pull down to map the FUS domains essential for RBM45-FUS interaction as in (F). Asterisks mean specific bands.