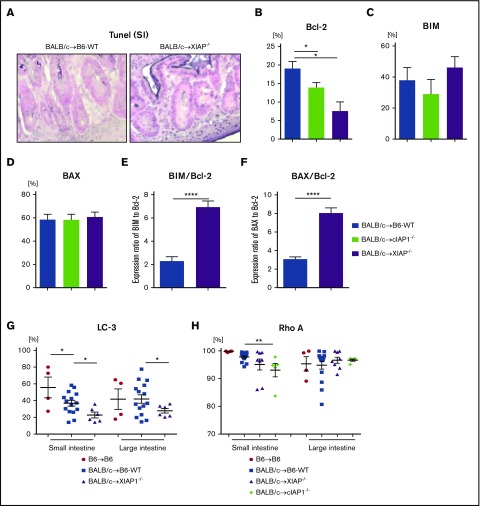
Figure 7.
IAPs on host target tissues coordinately regulate gut homeostasis by distinct mechanisms in GVHD. B6-WT and B6-XIAP−/− or cIAP1−/− animals received 10 Gy on day −1 and received transplants of 3 × 106 CD90.2+ splenic T cells along with 5 × 106 TCD-BM cells from either syngeneic B6 or allogeneic MHC-mismatched BALB/c donors. TUNEL staining and anti- or proapoptotic protein expression in intestinal epithelial cells were evaluated on day 7 after allo-BMT. (A) The representative figures of TUNEL staining of small intestine on day 7 after allo-BMT are shown. Original magnification ×40; TUNEL staining (nuclei purple) with a counterstain of Nuclear Fast Red (nuclei pink). (B-F) The expression of anti- or proapoptotic proteins in CD326+ intestinal epithelial cells on day 7 after allo-BMT: BCL-2 (B), BIM (C), BAX (D), and the ratios of BIM/BCL-2 (E) and BAX/BCL-2 (F). (G) LC3 expression in CD326+ intestinal epithelial cells from animals receiving transplants on day 7 after BMT was analyzed by FACS (n = 4-15, pooled from 3 independent experiments). *P < .05, **P < .01, ****P < .0001. The data are the means ± SEMs. (H) ρ-A expression in CD326+ intestinal epithelial cells from animals receiving transplants on day 7 after BMT was analyzed by FACS (n = 4-15, pooled from 3 independent experiments). **P < .01, when compared between allogeneic B6-WT and cIAP−/− animals. The data are the means ± SEMs.