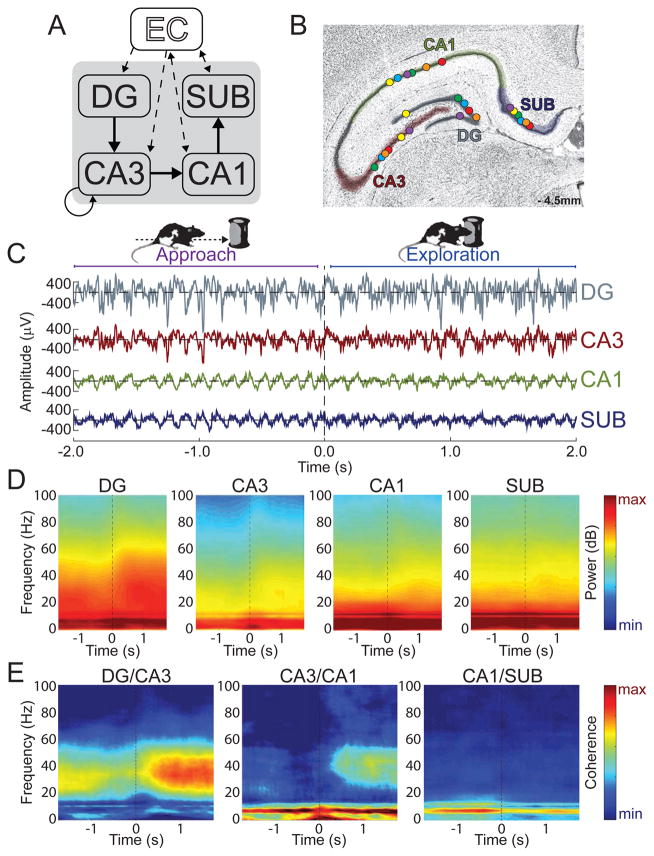
Figure 1. Slow gamma coherence increased while rats explored novel objects.
(A) Illustration of the serial connections of the hippocampal subregions [DG, CA3, CA1, and SUB (subiculum)] as well as its connections with the entorhinal cortex (EC). (B) Coronal hippocampal section showing LFP recording locations (circles) for each rat (different colors) in each of the four targeted subregions. (C) Example LFP data as a rat approached (< 0 s) and explored ( > 0 s) a novel object. (D) Moving window spectrograms for each hippocampal subregion time-locked to the initiation of novel object exploration (0 s). Minimum and maximum power values in decibels are noted on each spectrogram. (E) Moving window coherograms for each pair of directly connected hippocampal subregions time-locked to the initiation of novel object exploration (0 s). Increased coherence and power in the slow gamma range were apparent for DG/CA3 and CA3/CA1 during Exploration relative to Approach.