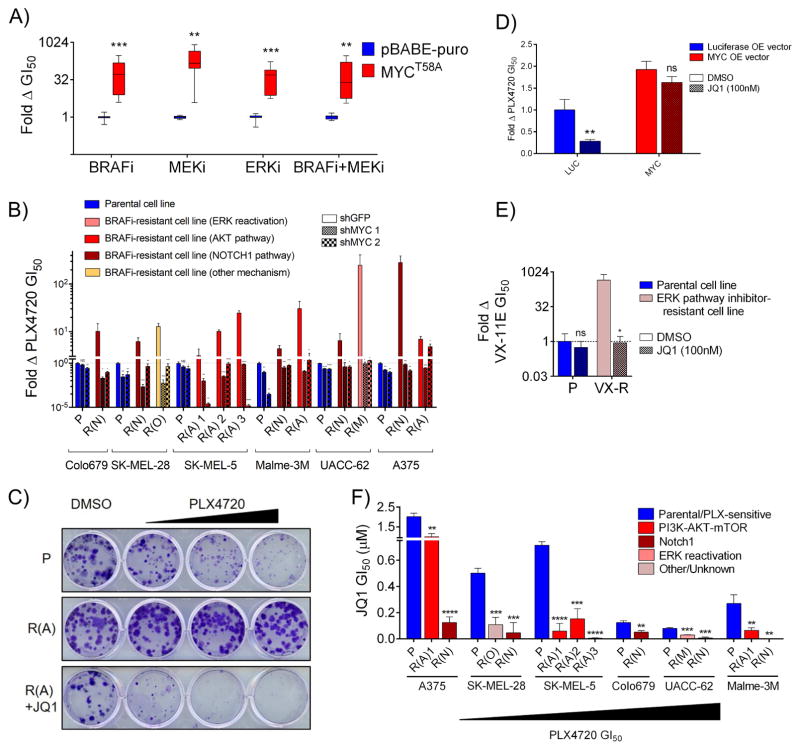
Figure 2. MYC activation is necessary and sufficient for resistance to BRAF/MEK pathway inhibitors in diverse BRAF-mutant melanoma cell lines.
A) Fold change in GI50 values for cells expressing MYCT58A and treated with either PLX4720, AZD6244, VX-11E, or the combination of PLX4720 and AZD6244 at a 1:1 dose ratio as compared to cells expressing an empty vector control (pBABE-puro). B) Fold change in GI50 values for PLX4720 between cell lines expressing shGFP compared to each of two independent shRNAs targeting MYC. P values denote significance between the response of shGFP and each shMYC expressing cell line. Parental lines are shaded blue, resistant lines, red/yellow. C) Clonogenic growth assay of A375 line derivatives treated with DMSO, 100 nM, 300 nM or 1 μM PLX4720 +/− 300 nM JQ1. D) WM793 cells expressing ectopic MYC or luciferase control were treated with DMSO or 100nM JQ1 and their PLX4720 GI50 value was determined. JQ1+PLX4720 treated cells are normalized to the viability of cells treated with JQ1 alone to account for nonspecific toxicity. P values denote significance between DMSO and JQ1 treatment in each cell line. E) Clonogenic growth of SK-MEL-5 cells with resistance to VX-11E (VX) in DMSO or 100 nM JQ1. JQ1+VX-11E treated cells are normalized to the viability of cells treated with JQ1 alone to account for nonspecific toxicity. P values denote significance between DMSO and JQ1 treatment. F) JQ1 GI50 values for the indicated PLX-resistant lines compared to matched parental controls. Significance is between the parental cell line and each matched resistant derivative. Data are means (SD) from 3 experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001. See also Figure S2.