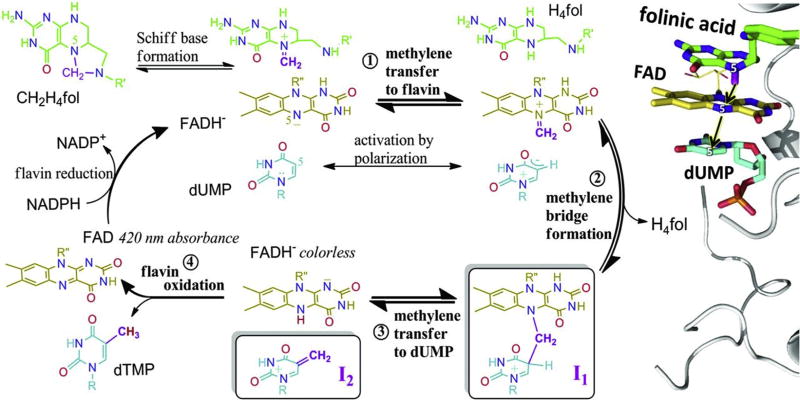
Fig. 6.
Proposed chemical mechanism for FDTS. (Left) Methylene to be transferred to N5 of flavin is in purple. Hydride on N5 reduced flavin is in red. (Right) Active site of TmFDTS (PDB ID 4GTA) with bound dUMP, FAD and folinic acid, a stable analogue of CH2H4folate. For clarity, the carbonyl oxygen of folinic acid is omitted. The structure is inverted to match the orientation of ligands in the left mechanism. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [26].