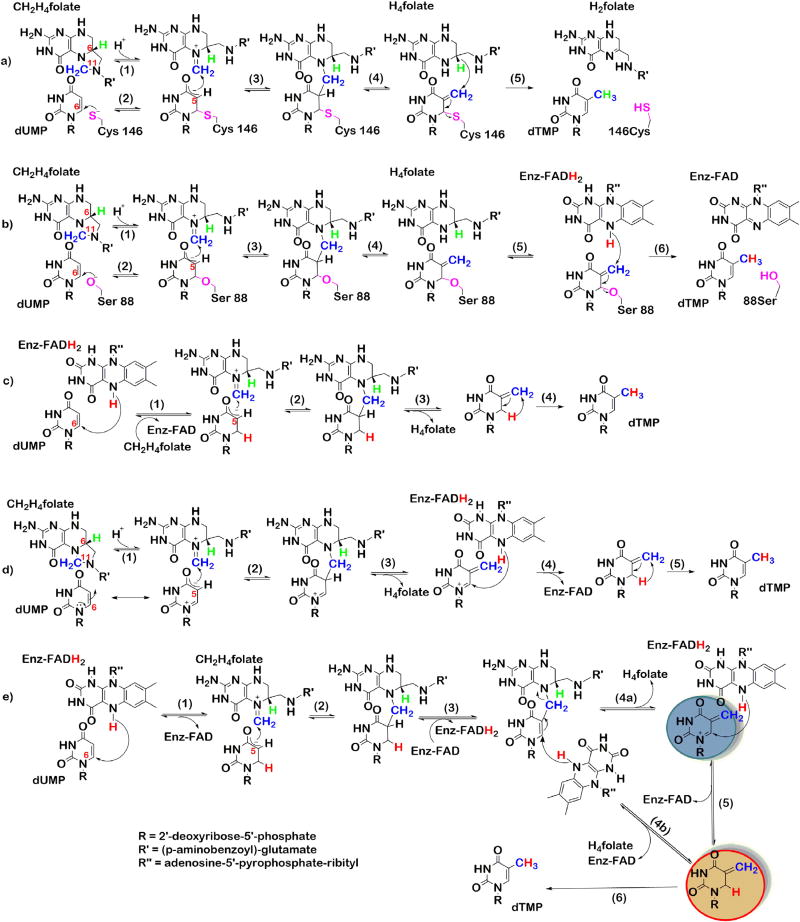
Scheme 3.
TSase mechanisms; a). classical TSase. b). FDTS where serine acts as the nucleophile. c). mechanism for FDTS where hydride of flavin acts as the nucleophile. d). substrate polarization in the active-site of FDTS. e). mechanism that combines c and d to explain the proton exchange at C5 of dUMP. Adapted with permission from Ref. [29].