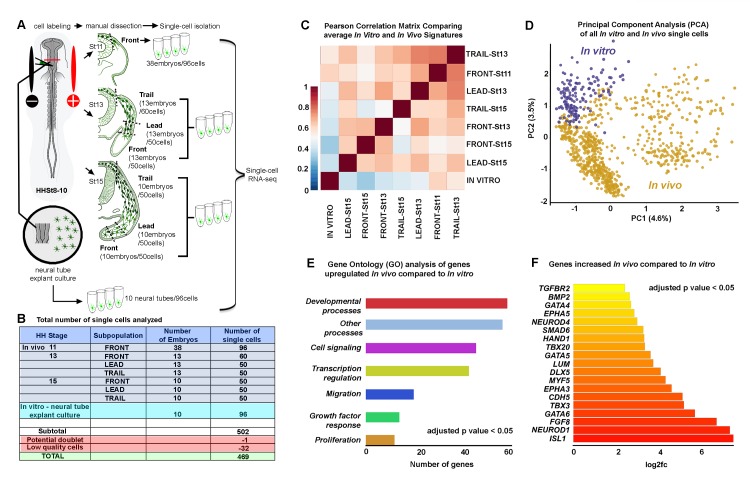
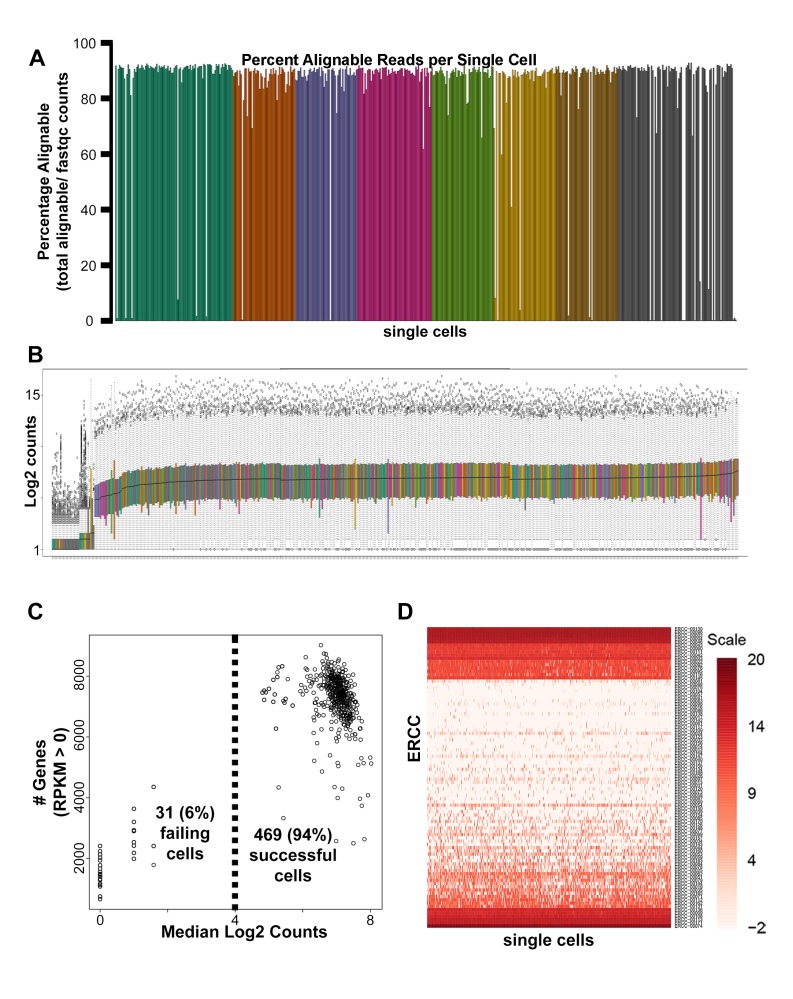
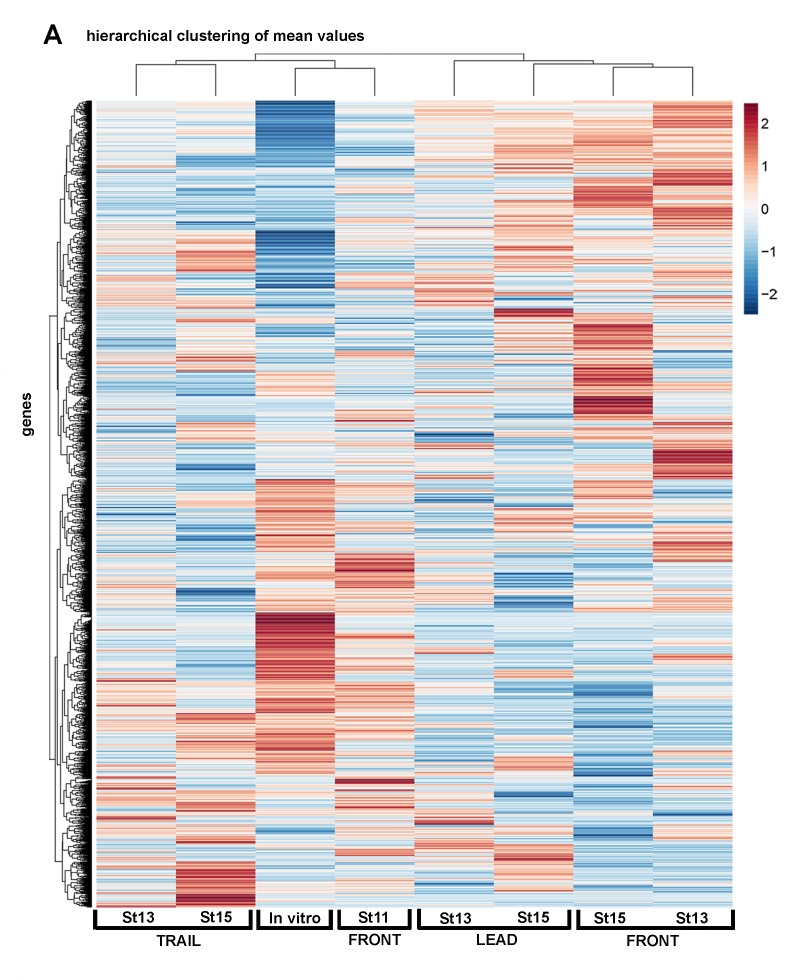
Figure 2. Single-cell RNA-seq shows in vitro and in vivo neural crest have distinct molecular signatures.
(A) Schematic representation of method used for harvesting samples from the cranial NC stream. Front is the ventral-most 5% of NC cells. Lead is the 25% of NC cells immediately following the Front cells. Trail is the remaining dorsal-most 70% of NC cells. Neural crest cells grown in vitro overnight from isolated neural tubes were also isolated for this analysis. (B) Numbers of single cells isolated from different subpopulations. (C) Pearson correlation matrix of the average expression profiles, based upon all differentially expressed genes all subpopulations analyzed (n = 1355 genes). (D) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of all in vitro and in vivo single cells using all differentially expressed genes (n = 1355 genes). (E) Condensed Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of genes upregulated in in vivo NC cells compared to in vitro NC cells (n = 806 genes). (F) Bar chart displaying NC relevant genes increased in in vivo NC cells compared to in vitro NC cells. HH, Hamburger and Hamilton (1951); St, stage.