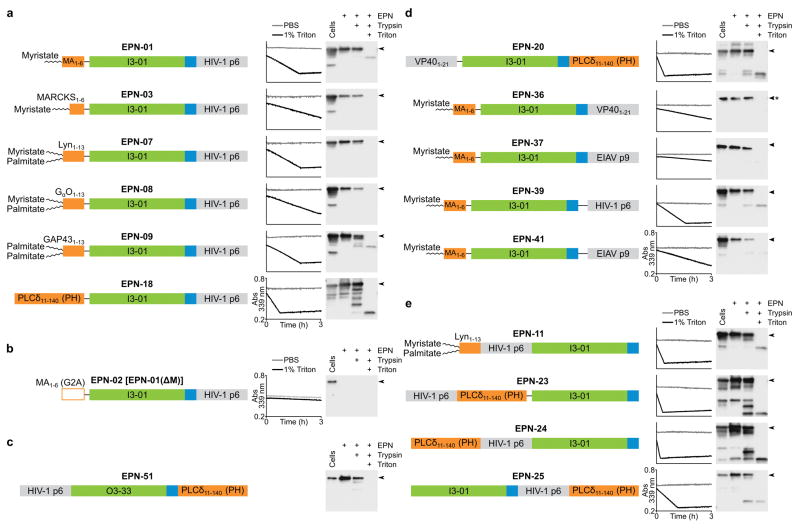
Extended Data Figure 8. Aldolase and protease protection assays for EPNs with a variety of functional elements and protein architectures.
Schematic illustrations and analyses of the 16 EPN constructs that yielded robust EPN biogenesis are shown, as well as one negative control. Each panel shows the construct, a representative plot of aldolase activity in the presence (black line) and absence (grey line) of detergent, and a western blot analysis of the protease protection assay. Arrowheads next to each blot denote the full-length protein. Aldolase activity was monitored by disappearance of absorbance at 339 nm. a, Different membrane-binding elements support EPN formation. b, EPN-02, also referred to as EPN-01(ΔM), is a negative control construct in which the myristoylation site was inactivated by mutation. Both assays reveal that EPN-02 protein was not released from cells. c, EPN-51, which uses the designed 24-subunit protein assembly O3-33 as a self-assembly domain, forms an EPN with an intact membrane envelope. The aldolase assay was not included because O3-33 is not an aldolase. d, Different ESCRT-recruiting elements can support EPN formation. The asterisk next to the blot of EPN-36 signifies that the blot was overexposed: EPN-36 reproducibly yielded fainter bands on western blots than would be expected based on its aldolase activity and analyses of SDS-PAGE gels stained with Coomassie. e, Membrane-binding, self-assembly, and ESCRT-recruiting elements can function from different positions within EPN constructs. EPN-11 is a permutation of EPN-07, while EPN-23, EPN-24, and EPN-25 are permutations of EPN-18.