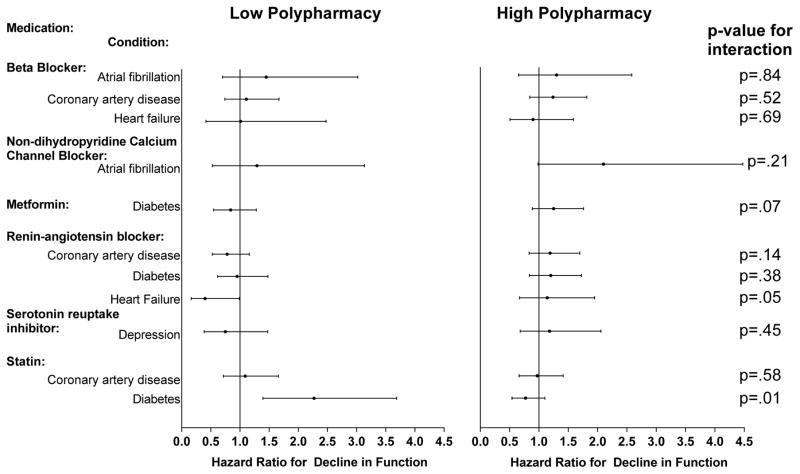
Figure 2. Adjusted Hazard Ratios for Decline in Physical Function by Guideline-Recommended Medication and Condition Stratified by Low and High Polypharmacy.
The displayed hazard ratios reflect the effect of taking the medication for a specific condition versus not taking the medication and are adjusted for the covariates which included demographics, insurance, geriatric impairments, health behaviors, hospitalizations, medications (other guideline-recommended), the other study conditions and Elixhauser comorbidity scale. Decline in physical function defined as a decrease in the number of activities (writing/handling objects, extending arms above shoulder, stooping/kneeling/crouching, lifting/carrying 10 pounds, walking ¼ mile or 2–3 blocks) the participant was able to perform as compared to the baseline. Eight respondents who could not do any of the 5 activities were excluded since they could not decline.
Low polypharmacy defined as < 7 and High Polypharmacy as >=7 concomitant medications.