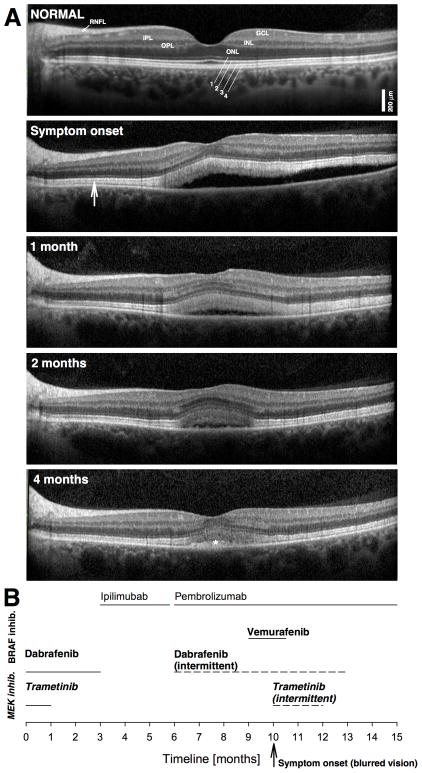
Figure 2.
A. SD-OCT horizontal cross-sections of the left eye of the patient at presentation compared with appearance on follow up visits. Hyporeflective (dark) nuclear layers labeled on the normal subject (ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer) are delimited by highly reflective synaptic layers (IPL, inner plexiform layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer) and the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). Outer photoreceptor/RPE laminae are labeled (1, external limiting membrane; 2, ellipsoid zone; 3 interdigitation between photoreceptor outer segment tips and RPE; cells; 4, RPE), following conventional terminology. A widened hyperreflective band sclerad to the ellipsoid zone layer is more prominent centrally but extends to regions without obvious neurosensory detachment (vertical arrow). A normal SD-OCT cross-section is shown for comparison. B. Time line of treatments; MEK inhibitors in bold and italics letters; BRAF inhibitors in bold.