Figure 1.
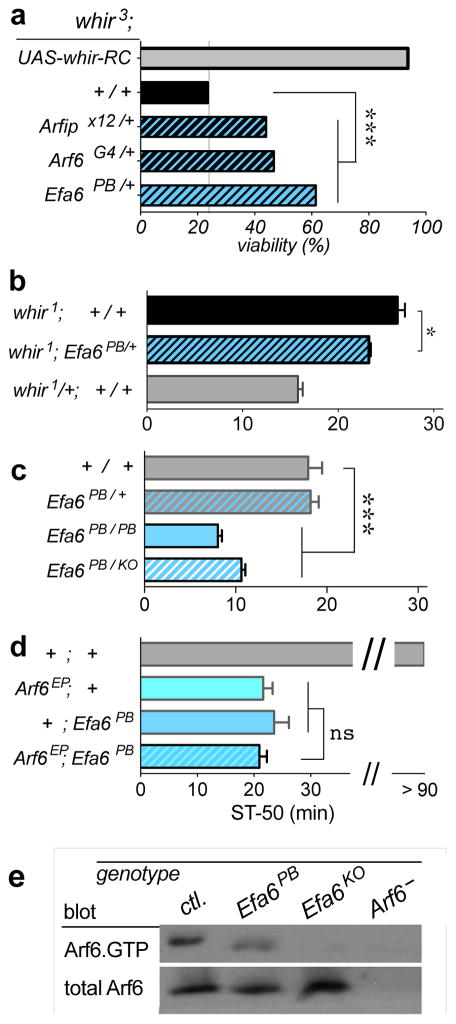
Efa6 mutant phenotypes. (a) Viability phenotypes of various whir3 genotypes. Displayed are the ratios of surviving whir3/Y;genotype males to whir3/+;genotype females. All the genotypes are in the context of the whir3 mutation, indicated by the whir3; atop. The whir3 allele causes semi-lethality (whir3;+/+, black bar), which can be rescued by re-introducing the RhoGAP18B-PC isoform (whir3;UAS-whir-RC, where RC is the RNA transcript encoding the PC protein isoform, grey bar) driven by the Gal4-driver inserted in the whir3 mutant. (Chi-square test with Bonferroni correction, z = 12.4, df = 153.6,1, P < 0.001, n = 1776 flies). This isoform also rescues the whir3-mediated ethanol resistance.31 Heterozygous Arfip/+, Arf6/+, and Efa6/+ mutations partially suppress the whir3 semi-lethality phenotype (df = 113.3,3, ***P < 0.001, n > 329 flies per genotype). (b) Heterozygous Efa6 mutation partially suppresses the ethanol-resistance phenotype of whir1 mutants (One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison vs. whir1, F(2,16) = 70.3, *P = 0.011, n = 8,5,6; top to bottom). In all of the Figures in this manuscript, error bars depicted are the standard error of the mean. Here, and in the following Figures, flies were exposed to 130/20 Ethanol/Air vapor (unless otherwise noted). Male flies were used in all behavioral experiments with the exception of whir1/+ females here (as the whir gene is on the X chromosome) and the females indicated in Supplementary Figures 2 and 3. (c) Homozygous Efa6PB mutants show significantly enhanced sensitivity to ethanol-induced sedation, as do Efa6PB/KO trans-heterozygous mutants (One-way ANOVA, with Dunnett’s multiple comparison vs. +/+ w− Berlin, F(3,33) = 48.0, ***P < 0.001, n = 6,7,11,13; top to bottom). The Efa6KO allele is a molecularly-targeted knock out, previously described.30 (d) Arf6;Efa6 double mutants are no more sensitive than either single mutant alone (F(2,33) = 4.6, ns P > 0.54, n = 12 per genotype). Flies were exposed to 30/120 Ethanol/Air, a low dose that did not sedate wild-type flies after 90 min. (e) Activated Arf6.GTP pull-down from head extracts, followed by anti-Arf6 Western blot. Both Efa6PB, and Efa6KO mutants show reduced Arf6 activation (and GTP-loading) compared to w− Berlin control (ctl.). Lysates from Arf6− flies contain undetectable levels of Arf6. A representative blot from 2 replicates is shown.