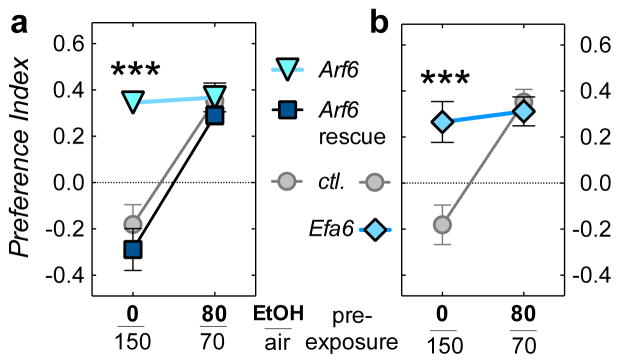
Figure 3.
Arf6 and Efa6 mutants show increased alcohol consumption preference. (a) Flies were offered a choice between liquid food, and liquid food containing 15% ethanol. Naïve wild-type flies (mock exposed to 0/150 Ethanol/Air) avoid ethanol (Preference Index < 0; w− Berlin ctl. flies). This changes to preference (PI > 0) after a 20 min 80/70 Ethanol/Air pre-exposure the day before (Two-way ANOVA, F(1,80)exposure = 44, P < 0.001, n =13,18,12,17,12,14, left to right, top to bottom). Arf6 mutants show high, naïve ethanol preference, independent of a pre-exposure (Dunnett’s post-hoc test, ***P < 0.001). This phenotype is rescued by UAS-Arf6-cDNA expression (Arf6 rescue, genotypes as in Figure 3A). (b) Efa6PB homozygotes display the same naïve preference phenotype (***P < 0.001, n = 13,18,12,12, left to right, top to bottom).