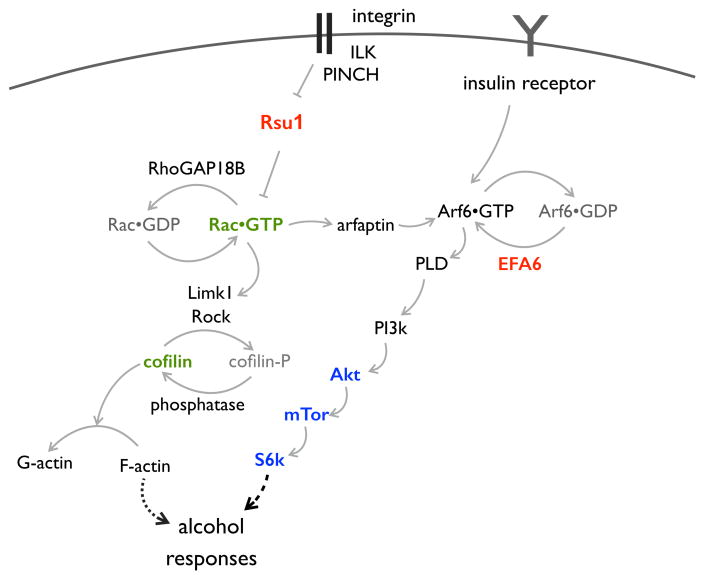
Figure 5.
Model of molecular mechanisms involved in Drosophila alcohol responses. Interactions (arrows) are based on our genetic and biochemical data19,21,25,31,40 (as well as other published data cited therein). Of particular relevance to this report: RhoGAP18B (encoded by the whir gene) binds to, and acts on Rac1.11,40 Rac1 is linked to Arf6 via Arfaptin, which binds to either activated GTPase.21 Here, we show that Efa6 is required for Arf6 activation and behavioral ethanol responses, and together, these biochemical data support our initial finding of a genetic interaction between whir and Efa6, placing them in the same network. Note that all molecules depicted here have mammalian orthologs, with the exception of RhoGAP18B, which contains a GTPase activating GAP domain and long stretches without any other characterized domains. Proteins whose genes are associated with human alcohol drinking are depicted in red (Rsu1,40 Efa6, this report), ones involved in rodent alcohol drinking in blue,27,60 and ones linked to rodent cocaine-induced behaviors in green (Rac1,cofilin).61,62 Abbreviations: ILK: integrin-linked kinase, PINCH: particularly interesting Cys-His rich protein, Rsu1: Ras-suppressor 1, Rac: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate, Limk1: LIM domain kinase 1, Rock: Rho-associated kinase, Arf6: ADP-ribosylation factor 6, PLD: phospholipase D, Akt: Thymona-associated kinase from the Ak strain, mTor: mechanistic target of rapamycin, S6k: S6 kinase.