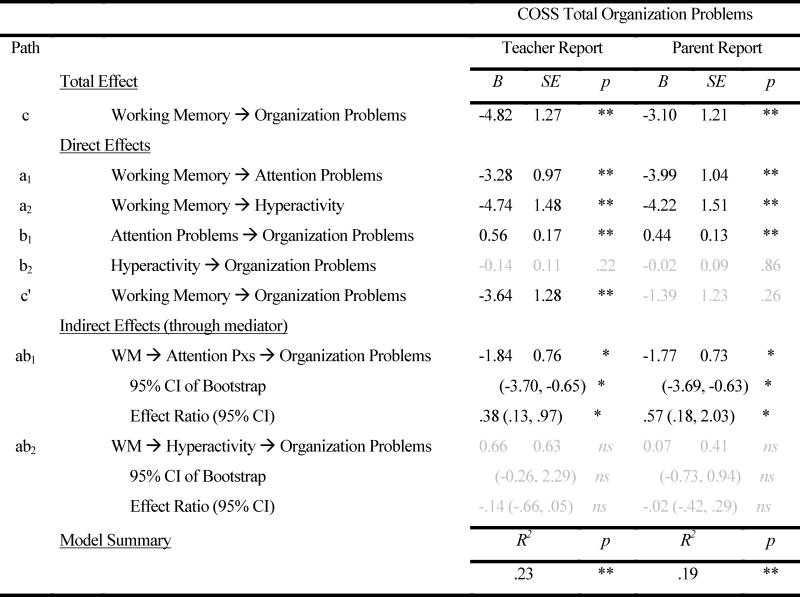
Table 2.
Impact of Working Memory and ADHD Symptoms on Total Organization Problems
Note: Bias-corrected bootstrapping was used for all analyses. Non-significant pathways are shown in
 font (95% CI includes 0.0). Parent-reported ADHD symptoms were tested as mediators of teacher-reported organizational problems, and vice versa. Paths labels reflect standard nomenclature (cf. Fritz & MacKinnon, 2007) and are depicted in Figure 1; c and c' reflect the total and direct effect of WM on organization problems before and after accounting for ADHD symptoms, respectively; Attn Px = Attention Problems, CE = Central Executive, Hyperact = Hyperactivity; WM = working memory;
font (95% CI includes 0.0). Parent-reported ADHD symptoms were tested as mediators of teacher-reported organizational problems, and vice versa. Paths labels reflect standard nomenclature (cf. Fritz & MacKinnon, 2007) and are depicted in Figure 1; c and c' reflect the total and direct effect of WM on organization problems before and after accounting for ADHD symptoms, respectively; Attn Px = Attention Problems, CE = Central Executive, Hyperact = Hyperactivity; WM = working memory;
p < .08,
p ≤ .05,
p ≤. 01
N = 73 due to skipped items on one teacher COSS.