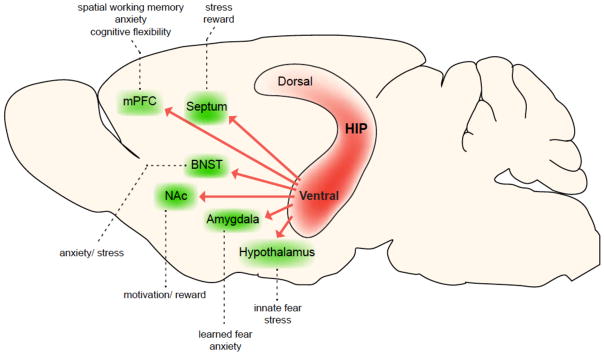
Figure 3.
Projections from the ventral HIP modulate distinct emotional behaviors. The ventral HIP sends direct projections to numerous structures that directly influence emotional behaviors (green structures indicate ventral HIP projection targets and dotted lines describe their putative behavioral consequences upon activation). These projections contribute to distinct aspects of behavior, such as spatial working memory through the mPFC, fear, anxiety and stress responses through the mPFC, amygdala, hypothalamus, septum and BNST, and reward-seeking behaviors through the NAc and septum. Moreover, there is evidence that many of these projections arise from largely non-overlapping cell populations within the CA1 pyramidal layer, including projections to the amygdala, mPFC, NAc, septum and lateral hypothalamus (Jin and Maren, 2015; Okuyama et al., 2016; Parfitt et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2016; Jimenez JC and Hen R, personal communication). Abbreviations: HIP, hippocampus; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; BNST, bed nucleus of stria terminalis; NAc, nucleus accumbens.