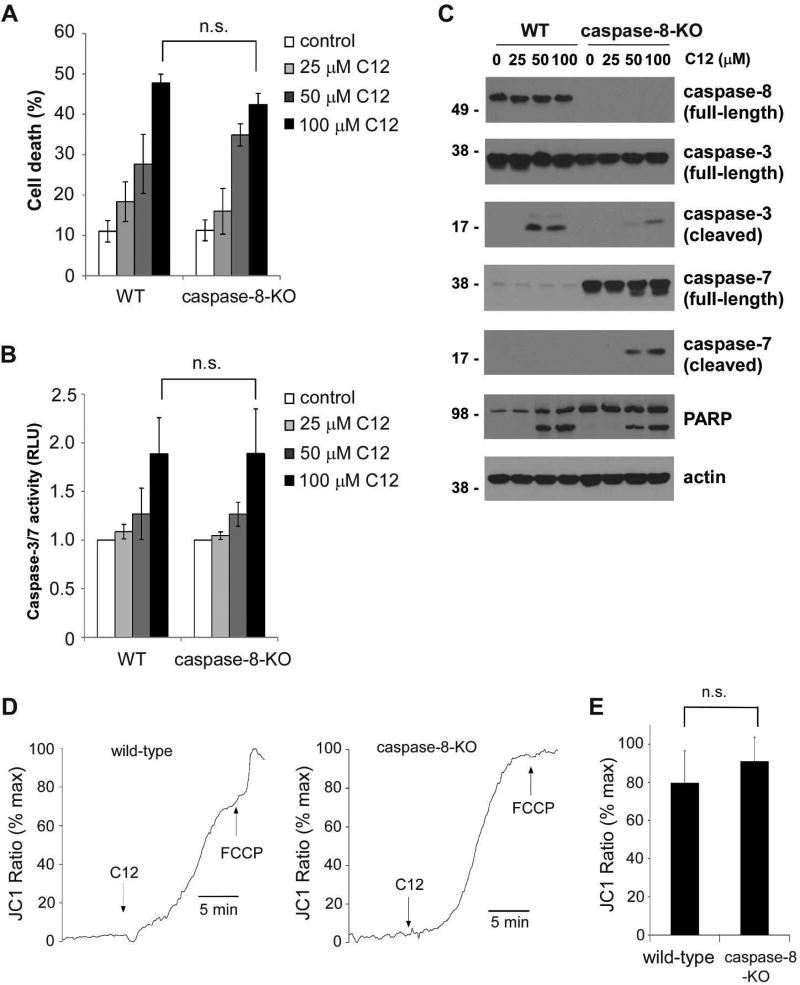
Figure 4. Caspase-8 activation is not involved in C12-induced apoptosis.
(A) The cytotoxicity of C12 on wild-type (WT) and caspase-8-KO MEFs was assessed 24 hours after treatment. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments with duplicate samples measured in each independent experiment. (B) Caspase-3/7 activities were evaluated 24 hours after C12 treatment. Data are shown as means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments with duplicate samples measured in each independent experiment. (C) Upon the treatment of C12 for 12 hours, cleavage of caspase-3 and caspase-7 in WT and caspase-8-KO MEFs was evaluated by western blot. The data shown are typical of three independent experiments. The molecular weight markers are labeled on the left (kD). (D) Mitochondrial membrane potentials of WT and caspase-8-KO MEFs loaded with JC1 were determined by fluorescence microscopy upon treatment with 50 µM C12 and 10 µM FCCP. The increase in JC1 fluorescence was equivalent to depolarization of Δψmito, which was observed in both WT and caspase-8-KO MEFs upon C12 exposure. The data are normalized as the percentage of maximal JC1 fluorescence increase evoked by FCCP. Typical results from three independent experiments are shown. (E) C12 caused equivalent mitochondrial depolarization in WT and caspase-8-KO MEFs. The summary of the data shown in (D) is presented. The value of steady-state depolarization of Δψmito caused by C12 in WT and caspase-8-KO MEFs was plotted as the percentage of the value of maximal depolarization of Δψmito caused by FCCP. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. ns, no significance. Student's unpaired t test.