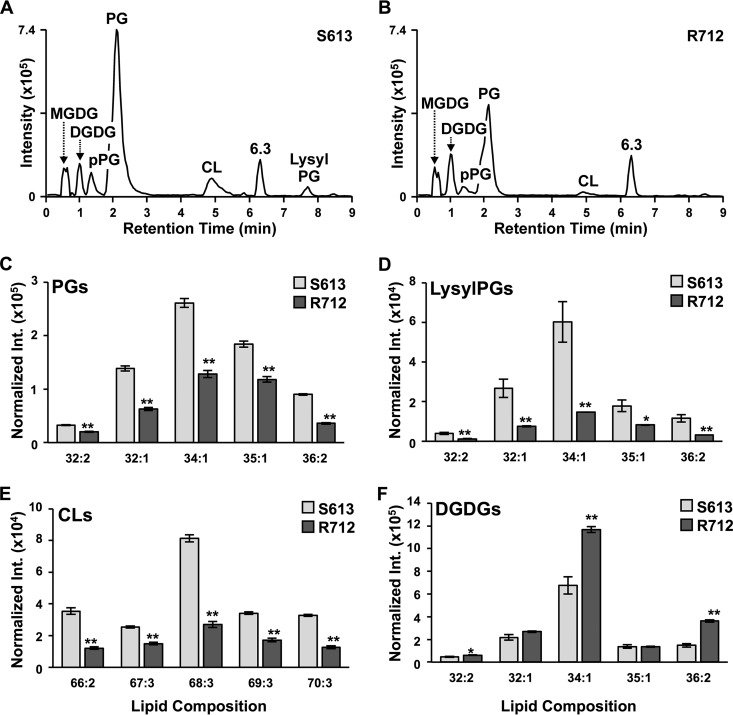
FIG 2 .
Results of the analysis of E. faecalis strains S613 and R712 by the HILIC-IM-MS lipidomics method. Negative-mode IM-XICs for daptomycin-susceptible E. faecalis strain S613 (raw intensity of 82-mg dry pellet shown) (A) and daptomycin-resistant E. faecalis strain R712 (raw intensity of 69-mg dry pellet shown) (B) reveals that the predominant lipid species in E. faecalis are PGs, CLs, DGDGs, MGDGs, and lysyl-PGs. PG (C), lysyl-PG (D), and CL (E) species are reduced in R712 regardless of the FA composition. (F) Individual DGDG species are reduced in R712 in a manner that is dependent upon the FA composition. Data shown in panels C to F are normalized to dry pellet weight. The FA compositions of individual lipid species were determined (total carbon number and unsaturation degree of the FAs in each lipid are shown; detailed FA compositions can be found in supplemental material), and the statistical significance of differences in intensity (Int.) was determined by Student's t test. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.005.