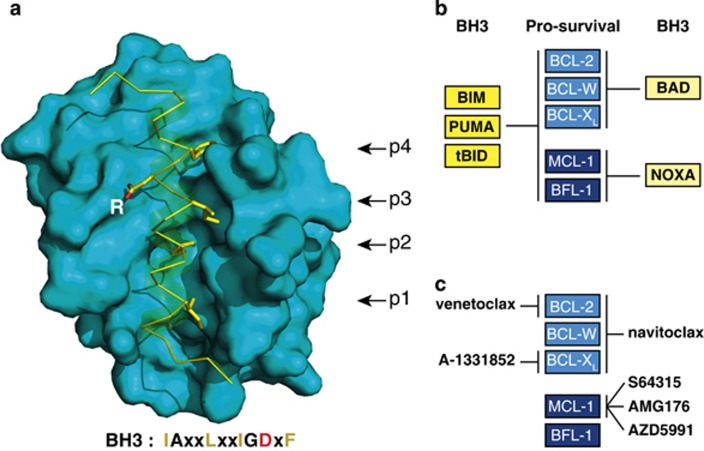
Figure 2.
Interaction of BCL-2 family members. (a) The canonical BH3/surface groove interaction in the family. Structure of BCL-XL (blue surface representation) bound to the amphipathic helical BH3 peptide of BIM (a yellow ribbon indicates its helical structure)27 (PDB/3FDL), with its N terminus at the bottom. Underneath the protein is a consensus BH3 sequence of the pro-apoptotic proteins (x denotes nonconserved residues). The four key hydrophobic amino acids (yellow) of the Bim BH3 peptide that bind to pockets p1 to p4 in BCL-XL are highlighted, as is the invariant aspartic acid (D) (oxygens in red) that binds to a conserved arginine (R) in BCL-XL. BIM or BID BH3 peptides associate with the grooves of BAX or BAK through contacts resembling those with their pro-survival relatives (as above) but include additional contacts that contribute to their activator function.41, 42, 43, 44 (b) Selective association of BH3-only proteins with their pro-survival relatives. Whereas BIM, PUMA and tBID bind promiscuously, BAD and NOXA have restricted targets, as indicated. (c) BCL-2 pro-survival targets of current BH3 mimetic drugs. A BH3 mimetic engages the surface groove of the targeted pro-survival protein(s) in a manner akin to their natural antagonists, as in (a), but usually involving only pockets p2 and p4. In cells, binding of the compound to their pro-survival target(s) releases any bound BH3-only proteins and prevents the targeted pro-survival protein(s) from restraining BAX and BAK. Note that preclinical studies were reported on Servier MCL-1 inhibitor S63845,115 but the clinical candidate from Novartis/Servier is the more advanced derivative S64315. Modified, with permission, from Figure 2 of Cory et al.8