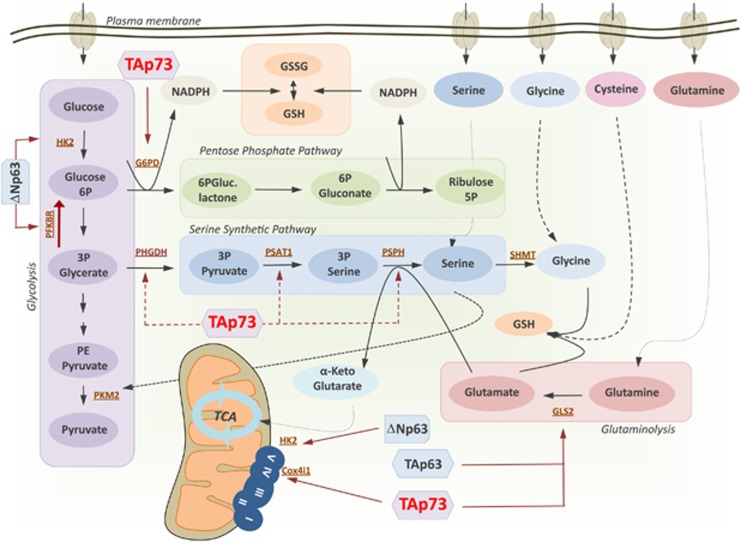
Figure 3.
Influence of p73/p63 on the major metabolic pathways. P63 and p73 both promote a general increase in glucose catabolism, resulting in an increase in diverting anabolic pathways and mitochondrial respiration. Activation of serine biosynthesis and the PPP by TAp73, ΔNp63 and TAp63 facilitates the antioxidant response through increased synthesis of GSH and regeneration of reduced GSH. Conversely, a reduced function of TAp73 and ΔNp63 negatively influences mitochondrial respiration, leading to electron leaks and oxidative stress. Overall, p53 family member function on cellular metabolism appears a critical process for maintaining the cellular redox balance, which has important implications for a number of different biological processes in tumor suppression, stress response and development. GSSG, oxidized GSH