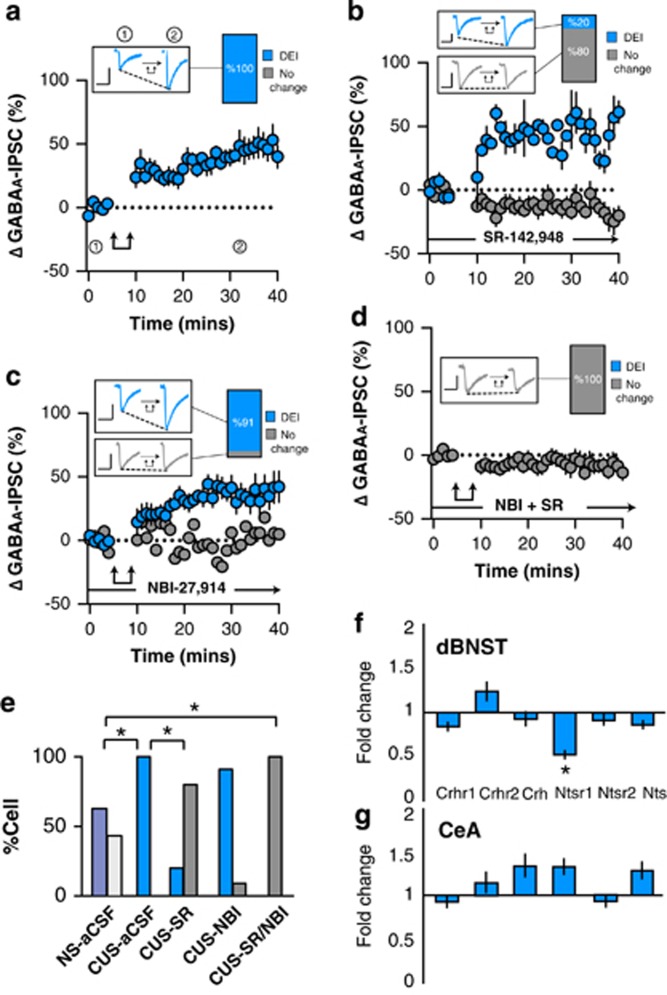
Figure 2.
Effect of post-synaptic depolarization on GABAA synaptic transmission in the ovBNST of chronic unpredictable stress (CUS)-exposed rats. Effect of post-synaptic activation on the amplitude of electrically evoked GABAA-IPSCs over time in the ovBNST of CUS rats in (a) aCSF, (b) with extracellular SR-142948 (10 μM), (c) with extracellular NBI-27914 (1 μM), and (d) with extracellular NBI-27914 (1 μM) and SR-142948 (10 μM). Insets in a–d show representative ovBNST-evoked GABAA-IPSCs before and after post-synaptic activation followed by the proportion of responding neurons. Scale bar: 250 pA and 25 ms. Double arrows represent post-synaptic depolarization (0 mV, 100 ms at 2 Hz, 5 min). (e) Histogram summarizing the proportion of responding neurons to post-synaptic depolarization across different pharmacological treatments. (f, g) Histogram showing fold change in mRNA expression of Crhr1, Crhr2, Crh, Ntsr1, Ntsr2, and Nts in CUS compared to NS rats in the dBNST and CeA. *p<0.05.