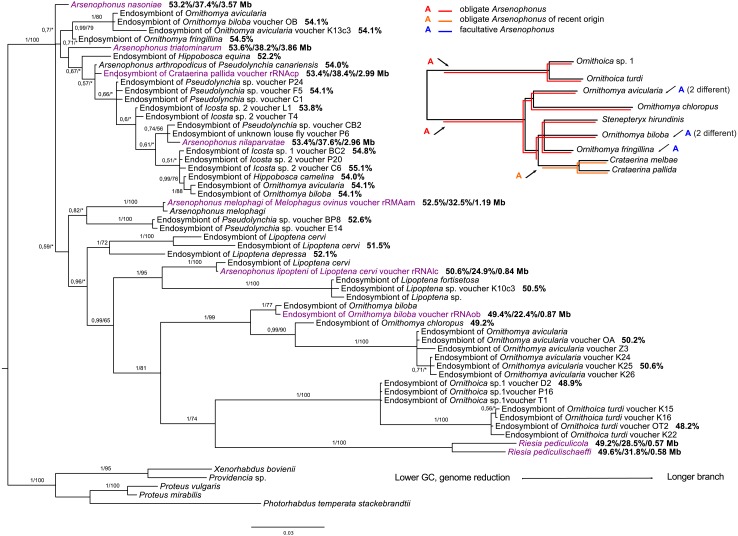
Figure 2. 16S rRNA phylogeny of Arsenophonus in Hippoboscidae inferred by BI analysis.
Posterior probabilities and bootstrap support are printed upon branches, respectively (asterisk was used for very low or missing bootstrap branch support). Taxa labelled with voucher are newly sequenced in this study. Genomic sequences are labelled with rRNA. Taxa in dark purple represent Arsenophonus bacteria which genome was sequenced. Numbers behind these taxa correspond to their GC content of 16S rRNA, GC content of genome, and genome size, respectively. Numbers behind other taxa correspond to GC content of their 16S rRNA. The smaller picture on the right side represents host phylogeny to which symbiont phylogeny was compared. Red lineages correspond to obligate symbionts while orange lineage is symbiont of recent origin. The blue A represent likely facultative Arsenophonus infection. To achieve this, we also used the information available on groEL gene by Morse et al. (2013) and Duron et al. (2014). Phylogenetic reconstructions of Arsenophonus of entire Hippoboscoidea and all Arsenophonus bacteria are included in Figs. S9 and S10.