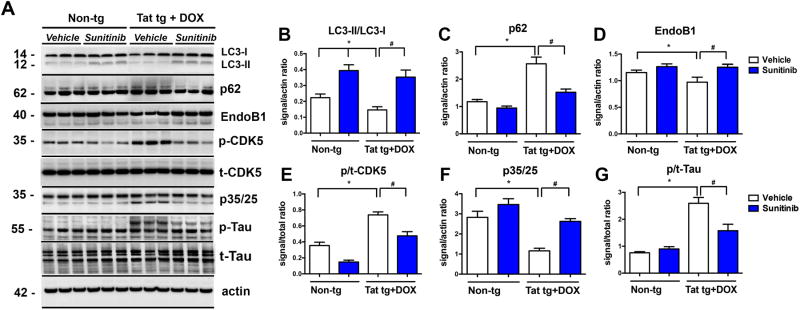
Fig 5. Immunoblot analysis of autophagy markers in Tat tg mice treated with sunitinib.
Doxycycline (DOX)-dependent GFAP-Tat tg mice were treated with DOX for 2 weeks to express Tat, and then treated with vehicle or sunitinib for 4 weeks8 mice were used per group and were 6.5-7.5 months of age when DOX treatment began. (A) Representative Western blot of LC3-II (12 kDa) and LC3-1 (14 kDa), p62 (doublet at ∼62 kDa), EndoB1 (doublet at 40 kDa), p-CDK5 (singlet at 35 kDa), p35/25 (doublet at ∼35 kDa), and pTau (at ∼55 kDa, with triplet in the vehicle-treated Tat tg mice, and doublet in the other groups). (B) Computer-aided analysis of LC3-II/LC3-I showed a significant increase in sunitinib-treated non-tg mice compared to vehicle-treated non-tg mice. Vehicle-treated Tat tg mice LC3-II/LC3-I levels were significantly decreased compared to vehicle-treated non-tg mice, and treatment with sunitinib significantly increased those levels compared to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice. (C) Computer aided analysis of p62 levels showed significant increase in vehicle-treated Tat tg mice compared to vehicle-treated non-tg mice. Treatment of Tat tg mice with sunitinib significantly decreased p62 levels compared to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice. (D) Computer-aided analysis of EndoB1 levels revealed a significant decrease in vehicle-treated Tat tg mice compared to non-tg vehicle-treated mice. Treatment with sunitinib significantly increased EndoB1 levels in Tat tg mice compared to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice. (E) Computer-aided analysis of p/tCDK5 levels showed a significant increase in vehicle-treated Tat tg mice compared to non-tg vehicle-treated mice. Treatment of Tat tg mice with sunitinib significantly decreased p/tCDK5 levels compared to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice. (F) Computer-aided analysis of p35/25 levels revealed a significant decrease in vehicle-treated Tat tg mice compared to vehicle-treated non-tg mice. Sunitinib treatment significantly increased p35/25 levels in Tat tg mice compared to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice. (G) Computer-aided analysis of p/tTau levels using the PHF1 antibody showed a significant increase in vehicle-treated Tat tg mice compared to vehicle-treated non-tg mice. Treatment with sunitinib significantly decreased p/tTau levels in Tat tg mice compared to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice. Statistical analysis performed using ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis using Dunnett's comparison to vehicle-treated non-tg mice (* = p-value < 0.05) or Tukey-Kramer comparison to vehicle-treated Tat tg mice (# = p-value < 0.05). (# = p-value < 0.05). N = 8 mice per treatment group.