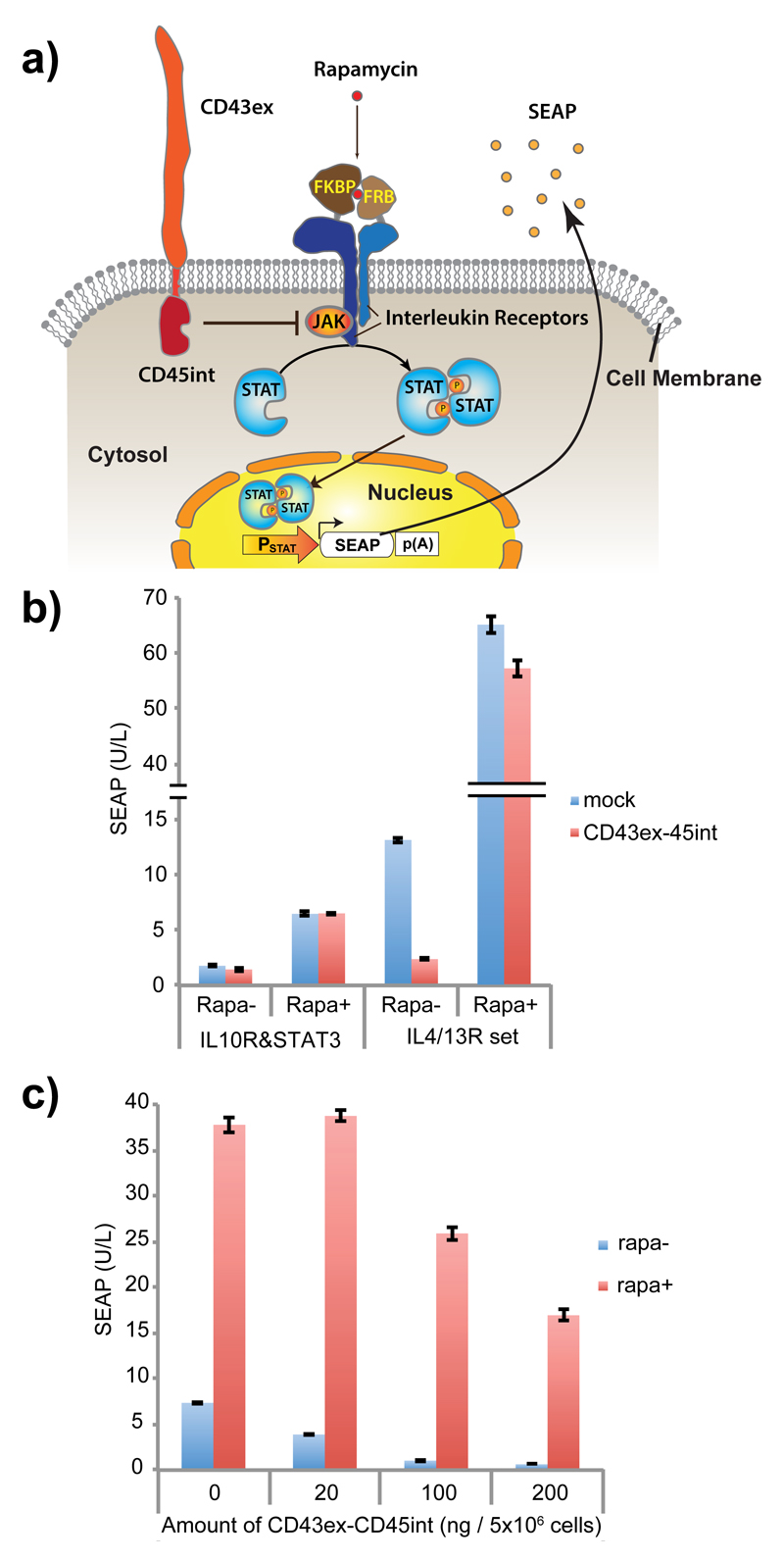
Figure 1. Evaluation of CD43ex-45int for suppressing cytokine receptor-mediated signaling pathways.
(a) Schematic illustration of the design. In the presence of rapamycin (rapa), Janus kinase (JAK) is activated by receptor dimerization, leading to phosphorylation and dimerization of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT). Dimerized STAT translocates to the nucleus, and promotes transgene expression via a STAT-responsive minimal promoter. The effect of co-expression of CD43ex-45int on signaling was determined by quantifying induced expression of a reporter protein, secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP). (b) SEAP expression from HEK-293T cells co-transfected with pRK96 (PhCMV-CD43ex-45int-pA) (pA: poly adenylation signal) (or pcDNA3.1(+) for mock) and interleukin receptors together with corresponding STAT and its reporter (IL10R & STAT3 set: pLeo56 (PhCMV-FKBP-IL10Rα-pA), pLeo57 (PhCMV-FRB-IL10Rβ-pA), pLS15 (PhCMV-STAT3-pA) and pLS13 (PSTAT3-SEAP-pA). IL4/13R & STAT6 set: pLeo53 (PhCMV-FKBP-IL4Rα-pA) and pLeo52 (PhCMV-FRB-IL13Rα1-pA), pLS16 (PhCMV-STAT6-pA), and pLS12 (PSTAT6-SEAP-pA)) (± rapa as inducer). (c) Dose-dependency of the inhibitory activity of CD43ex-45int on IL4/13R signaling. SEAP expression with different amounts of pRK96 is shown. All the data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments measured in triplicate (n=3).