In the title compound, the two indole ring systems are approximately perpendicular to one another, making a dihedral angle of 80.9 (5)°. In the crystal, pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into inversion dimers and these are further linked by N—H⋯O and hydrogen bonds and short Cl—Cl contacts into supramolecular chains.
Keywords: crystal structure, bisindole, MRI, contrast agent
Abstract
In the title compound, C29H24Cl2N2O4, the mean planes of the two indole ring systems (r.m.s. deviations = 0.1249 and 0.0075 Å) are approximately perpendicular to one another, with a dihedral angle of 80.9 (5)° between them. The benzene ring is inclined to the mean planes of the two indole ring systems by 76.1 (3) and 78.3 (4)°. Weak intramolecular C—H⋯π interactions affect the molecular conformation. In the crystal, pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into inversion dimers which are further linked into supramolecular chains by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and short Cl—Cl contacts.
Chemical context
Bis(indolyl)methane derivatives are abundantly present in various terrestrial and marine natural resources (Porter et al.,1977 ▸; Sundberg, 1996 ▸). They are important antibiotics in the field of pharmaceuticals with diverse activities, displaying anticancer, antileishmanial and antihyperlipidemic properties (Chang et al., 1999 ▸; Ge et al., 1999 ▸). Furthermore, bis(indolyl)methane derivatives can also be used as precursors for MRI necrosis avid contrast agents (Ni, 2008 ▸). In recent years, we have reported the synthesis and crystal structures of some similar bis(indoly)methane compounds (Sun et al., 2012 ▸, 2015 ▸; Li et al., 2014 ▸; Lu et al., 2014 ▸). We report here the molecular and crystal structure of the title bis(indoly)methane derivative.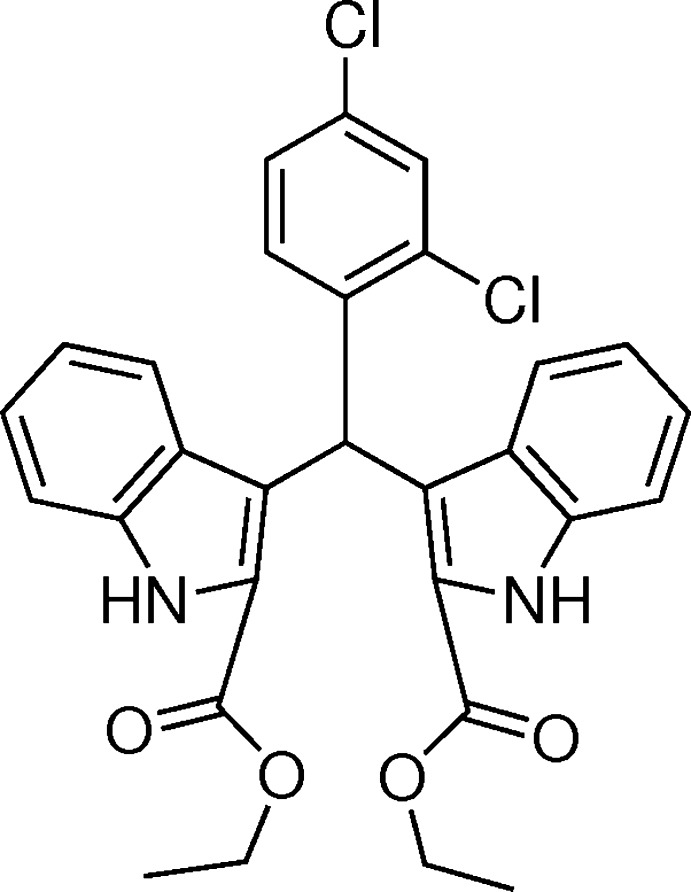
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The overall conformation of the molecule is affected by intramolecular C4—H4A⋯Cg5 and C15—H15A⋯Cg1 interactions (Cg1 and Cg5 are the centroids of the N1,C8,C3,C2,C9 and C24–C29 rings, respectively), Fig. 1 ▸, Table 1 ▸. The two indole ring systems are nearly perpendicular to one another, subtending a dihedral angle of 80.9 (5)° while the C24–C29 benzene ring is inclined to the N1/C2–C9 and N2/C13–C20 indole ring systems by dihedral angles of 76.1 (3) and 78.3 (4)°, respectively. The carboxyl groups lie close to the planes of the indole ring systems to which they are bound, with dihedral angles between the carboxyl groups and the mean planes of the N1/C2–C9 and N2/C13–C20 indole ring systems of 8.3 (5) and 5.6 (3)°, respectively.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. Intramolecular C—H⋯π(ring) contacts (Table 1 ▸) are shown as dotted black lines with ring centroids displayed as coloured spheres.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg5 are the centroids of the N1,C8,C3,C2,C9 and C24–C29 rings respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.07 | 2.864 (4) | 152 |
| N2—H2A⋯O4ii | 0.86 | 2.04 | 2.871 (4) | 161 |
| C11—H11A⋯Cl1iii | 0.97 | 2.81 | 3.731 (5) | 158 |
| C4—H4A⋯Cg5 | 0.93 | 2.77 | 3.516 (4) | 137 |
| C15—H15A⋯Cg1 | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.476 (5) | 139 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, pairs of N1—H1A⋯O1 and N2—H2A⋯O4 hydrogen bonds, Table 1 ▸, link the molecules into inversion dimers that form supramolecular chains along the b-axis direction. C11—H11A⋯Cl1 and short Cl2⋯Cl2 contacts [Cl2⋯Cl2(1 − x, 1 − y, −z) = 3.467 (2) Å] bridge these chains and form sheets of molecules parallel to ( 12), Fig. 2 ▸.
12), Fig. 2 ▸.
Figure 2.
A packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) and Cl⋯Cl contacts are shown as dashed lines.
Database survey
Several similar structures have been reported previously, i.e. diethyl 3,3′-(phenylmethylene)bis(1H-indole-2-carboxylate) (Sun et al., 2012 ▸), dimethyl 3,3′-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylene]bis(1H-indole-2-carboxylate) (Sun et al., 2015 ▸) dimethyl 3,3′-[(4-chlorophenyl) methylene]bis(1H-indole-2-carboxylate) (Li et al., 2014 ▸) and dimethyl 3,3′-[(3-fluorophenyl)methylene]bis(1H-indole-2-carboxylate) (Lu et al., 2014 ▸). In these structures, the two indole ring systems are also nearly perpendicular to one another, making dihedral angles of 82.0 (5), 84.0 (5), 79.5 (4) and 87.8 (5)°, respectively.
Synthesis and crystallization
Ethyl indole-2-carboxylate (1.88 g, 10 mmol) was dissolved in 20 ml ethanol; commercially available 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde (0.88 g, 5 mmol) was added and the mixture was heated to reflux temperature. Concentrated HCl (0.5 ml) was added and the reaction was left for 1 h. After cooling, the white product was filtered off and washed thoroughly with ethanol. The reaction was monitored with TLC (AcOEt:hexane = 1:3). Colourless block-like crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained in 92% yield by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were positioned geometrically with N—H = 0.86 Å and C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with U iso(H) = xU eq(C,N), where x = 1.5 for methyl H atoms and 1.2 for all others.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C29H24Cl2N2O4 |
| M r | 535.40 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.776 (2), 15.939 (3), 17.581 (4) |
| β (°) | 101.94 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 2680.2 (9) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.28 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 |
| Absorption correction | ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.921, 0.973 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 5221, 4917, 2864 |
| R int | 0.034 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.603 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.067, 0.192, 1.00 |
| No. of reflections | 4917 |
| No. of parameters | 328 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.69, −1.14 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017015730/sj5539sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017015730/sj5539Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017015730/sj5539Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1582719
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Center of Testing and Analysis, Nanjing University, for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C29H24Cl2N2O4 | F(000) = 1112 |
| Mr = 535.40 | Dx = 1.327 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 9.776 (2) Å | θ = 9–13° |
| b = 15.939 (3) Å | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| c = 17.581 (4) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 101.94 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 2680.2 (9) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | 2864 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.034 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 1.7° |
| ω/2θ scans | h = 0→11 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968) | k = 0→19 |
| Tmin = 0.921, Tmax = 0.973 | l = −21→21 |
| 5221 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 200 reflections |
| 4917 independent reflections | intensity decay: 1% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.192 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1P)2 + 0.670P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4917 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 328 parameters | Δρmax = 0.69 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −1.13 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.99326 (13) | 0.65116 (9) | 0.32372 (10) | 0.0997 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.0795 (3) | 0.57429 (17) | −0.06706 (15) | 0.0537 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.1566 (3) | 0.53608 (18) | 0.09007 (17) | 0.0440 (8) | |
| H1A | 0.0821 | 0.5101 | 0.0675 | 0.053* | |
| C1 | 0.4458 (4) | 0.6877 (2) | 0.0923 (2) | 0.0371 (8) | |
| H1B | 0.4656 | 0.6719 | 0.0418 | 0.044* | |
| Cl2 | 0.61986 (13) | 0.53457 (7) | 0.08076 (8) | 0.0813 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.2675 (3) | 0.65654 (16) | −0.05724 (14) | 0.0478 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.3672 (3) | 0.91230 (18) | 0.04635 (18) | 0.0458 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.3841 | 0.9599 | 0.0272 | 0.055* | |
| C2 | 0.3421 (4) | 0.6237 (2) | 0.1094 (2) | 0.0373 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.6370 (3) | 0.77571 (16) | 0.01095 (16) | 0.0514 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.3369 (4) | 0.5821 (2) | 0.1812 (2) | 0.0400 (8) | |
| O4 | 0.6115 (3) | 0.91368 (16) | −0.00828 (18) | 0.0600 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.4188 (4) | 0.5829 (3) | 0.2572 (2) | 0.0554 (11) | |
| H4A | 0.4952 | 0.6187 | 0.2702 | 0.066* | |
| C5 | 0.3842 (5) | 0.5301 (3) | 0.3120 (3) | 0.0628 (12) | |
| H5A | 0.4388 | 0.5304 | 0.3620 | 0.075* | |
| C6 | 0.2703 (5) | 0.4761 (3) | 0.2950 (3) | 0.0598 (12) | |
| H6A | 0.2510 | 0.4410 | 0.3337 | 0.072* | |
| C7 | 0.1858 (4) | 0.4738 (2) | 0.2225 (2) | 0.0526 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.1089 | 0.4382 | 0.2111 | 0.063* | |
| C8 | 0.2203 (4) | 0.5274 (2) | 0.1659 (2) | 0.0424 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.2289 (3) | 0.5925 (2) | 0.0549 (2) | 0.0379 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.1837 (4) | 0.6072 (2) | −0.0283 (2) | 0.0378 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.2406 (5) | 0.6680 (3) | −0.1409 (2) | 0.0611 (12) | |
| H11A | 0.1587 | 0.7029 | −0.1577 | 0.073* | |
| H11B | 0.2245 | 0.6142 | −0.1670 | 0.073* | |
| C12 | 0.3646 (5) | 0.7087 (3) | −0.1591 (3) | 0.080 | |
| H12A | 0.3509 | 0.7169 | −0.2143 | 0.120* | |
| H12B | 0.4449 | 0.6737 | −0.1418 | 0.120* | |
| H12C | 0.3789 | 0.7619 | −0.1333 | 0.120* | |
| C13 | 0.3873 (3) | 0.7766 (2) | 0.0822 (2) | 0.0367 (8) | |
| C14 | 0.2657 (4) | 0.8105 (2) | 0.1040 (2) | 0.0393 (8) | |
| C15 | 0.1617 (4) | 0.7797 (3) | 0.1419 (2) | 0.0499 (10) | |
| H15A | 0.1632 | 0.7241 | 0.1582 | 0.060* | |
| C16 | 0.0581 (5) | 0.8334 (3) | 0.1541 (3) | 0.0624 (12) | |
| H16A | −0.0111 | 0.8133 | 0.1786 | 0.075* | |
| C17 | 0.0542 (5) | 0.9170 (3) | 0.1308 (3) | 0.0755 (14) | |
| H17A | −0.0165 | 0.9517 | 0.1409 | 0.091* | |
| C18 | 0.1515 (4) | 0.9490 (3) | 0.0938 (3) | 0.0610 (12) | |
| H18A | 0.1474 | 1.0047 | 0.0776 | 0.073* | |
| C19 | 0.2575 (4) | 0.8959 (2) | 0.0809 (2) | 0.0430 (9) | |
| C20 | 0.4467 (4) | 0.8411 (2) | 0.0468 (2) | 0.0378 (8) | |
| C21 | 0.5712 (4) | 0.8480 (2) | 0.0141 (2) | 0.0410 (9) | |
| C22 | 0.7623 (5) | 0.7796 (3) | −0.0215 (3) | 0.0673 (13) | |
| H22A | 0.8306 | 0.8168 | 0.0093 | 0.081* | |
| H22B | 0.7397 | 0.8006 | −0.0744 | 0.081* | |
| C23 | 0.8196 (6) | 0.6929 (4) | −0.0202 (4) | 0.113 (2) | |
| H23A | 0.9022 | 0.6932 | −0.0417 | 0.170* | |
| H23B | 0.7509 | 0.6566 | −0.0505 | 0.170* | |
| H23C | 0.8427 | 0.6730 | 0.0325 | 0.170* | |
| C24 | 0.5846 (4) | 0.6817 (2) | 0.1501 (2) | 0.0391 (8) | |
| C25 | 0.6324 (4) | 0.7431 (2) | 0.2053 (2) | 0.0437 (9) | |
| H25A | 0.5790 | 0.7912 | 0.2068 | 0.052* | |
| C26 | 0.7582 (4) | 0.7340 (3) | 0.2582 (2) | 0.0530 (11) | |
| H26A | 0.7885 | 0.7758 | 0.2948 | 0.064* | |
| C27 | 0.8370 (4) | 0.6642 (3) | 0.2566 (3) | 0.0614 (12) | |
| C28 | 0.7963 (4) | 0.6021 (3) | 0.2019 (3) | 0.0634 (12) | |
| H28A | 0.8513 | 0.5547 | 0.2006 | 0.076* | |
| C29 | 0.6715 (4) | 0.6124 (2) | 0.1493 (2) | 0.0505 (10) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0617 (8) | 0.0762 (9) | 0.1361 (13) | −0.0114 (7) | −0.0373 (8) | 0.0215 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0412 (15) | 0.0659 (18) | 0.0512 (16) | −0.0065 (14) | 0.0034 (13) | 0.0008 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0394 (17) | 0.0439 (18) | 0.0467 (18) | −0.0081 (14) | 0.0045 (14) | 0.0025 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0398 (19) | 0.0283 (17) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0036 (15) | 0.0076 (16) | −0.0009 (15) |
| Cl2 | 0.0746 (8) | 0.0529 (7) | 0.1067 (10) | 0.0220 (6) | −0.0039 (7) | −0.0310 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0522 (15) | 0.0472 (15) | 0.0421 (15) | −0.0103 (13) | 0.0050 (12) | 0.0081 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0482 (18) | 0.0284 (15) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0026 (14) | 0.0178 (16) | 0.0064 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0386 (19) | 0.0289 (18) | 0.044 (2) | −0.0002 (15) | 0.0090 (17) | 0.0012 (15) |
| O3 | 0.0497 (16) | 0.0397 (14) | 0.0711 (18) | 0.0091 (12) | 0.0271 (14) | 0.0049 (13) |
| C3 | 0.044 (2) | 0.0314 (18) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0024 (16) | 0.0090 (17) | 0.0068 (16) |
| O4 | 0.0536 (17) | 0.0404 (15) | 0.094 (2) | 0.0019 (13) | 0.0339 (16) | 0.0158 (15) |
| C4 | 0.058 (3) | 0.056 (2) | 0.050 (2) | −0.012 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| C5 | 0.061 (3) | 0.070 (3) | 0.054 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.018 (2) |
| C6 | 0.063 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.023 (2) |
| C7 | 0.050 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.063 (3) | −0.0070 (19) | 0.017 (2) | 0.011 (2) |
| C8 | 0.039 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0003 (16) | 0.0113 (17) | 0.0015 (17) |
| C9 | 0.0347 (18) | 0.0327 (18) | 0.047 (2) | −0.0003 (15) | 0.0107 (16) | 0.0019 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0344 (19) | 0.0329 (18) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0045 (16) | 0.0061 (17) | −0.0003 (16) |
| C11 | 0.058 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.052 (3) | −0.007 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.016 (2) |
| C12 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.000 | 0.017 | 0.000 |
| C13 | 0.0364 (19) | 0.0316 (18) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0024 (15) | 0.0072 (16) | −0.0020 (15) |
| C14 | 0.040 (2) | 0.0365 (19) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0038 (16) | 0.0105 (16) | −0.0017 (16) |
| C15 | 0.046 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.058 (3) | 0.0015 (19) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0061 (19) |
| C16 | 0.059 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.078 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C17 | 0.064 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.114 (4) | 0.021 (2) | 0.042 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C18 | 0.056 (3) | 0.041 (2) | 0.093 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C19 | 0.040 (2) | 0.038 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0029 (17) | 0.0158 (18) | 0.0010 (17) |
| C20 | 0.0388 (19) | 0.0288 (18) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0016 (15) | 0.0097 (16) | −0.0008 (15) |
| C21 | 0.039 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.045 (2) | −0.0015 (17) | 0.0076 (17) | 0.0001 (17) |
| C22 | 0.063 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.089 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.041 (3) | 0.002 (2) |
| C23 | 0.102 (4) | 0.099 (5) | 0.158 (6) | 0.055 (4) | 0.071 (4) | 0.029 (4) |
| C24 | 0.038 (2) | 0.0334 (18) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0048 (16) | 0.0095 (16) | 0.0011 (16) |
| C25 | 0.045 (2) | 0.0338 (19) | 0.052 (2) | −0.0043 (17) | 0.0096 (18) | 0.0023 (17) |
| C26 | 0.060 (3) | 0.043 (2) | 0.052 (2) | −0.018 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0031 (18) |
| C27 | 0.045 (2) | 0.052 (3) | 0.080 (3) | −0.008 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.016 (2) |
| C28 | 0.042 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.097 (4) | 0.005 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C29 | 0.046 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.069 (3) | 0.0024 (18) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0040 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C27 | 1.738 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| O1—C10 | 1.221 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| N1—C8 | 1.356 (5) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C9 | 1.368 (4) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C13—C20 | 1.389 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.511 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.429 (5) |
| C1—C24 | 1.521 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.414 (5) |
| C1—C13 | 1.525 (4) | C14—C19 | 1.418 (5) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C15—C16 | 1.377 (5) |
| Cl2—C29 | 1.730 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C10 | 1.312 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.392 (6) |
| O2—C11 | 1.450 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C19 | 1.363 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.358 (6) |
| N2—C20 | 1.375 (4) | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C18—C19 | 1.393 (5) |
| C2—C9 | 1.396 (5) | C18—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.436 (5) | C20—C21 | 1.454 (5) |
| O3—C21 | 1.327 (4) | C22—C23 | 1.489 (7) |
| O3—C22 | 1.456 (5) | C22—H22A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.409 (5) | C22—H22B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C8 | 1.415 (5) | C23—H23A | 0.9600 |
| O4—C21 | 1.212 (4) | C23—H23B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.372 (5) | C23—H23C | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C24—C25 | 1.389 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (6) | C24—C29 | 1.396 (5) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C25—C26 | 1.388 (5) |
| C6—C7 | 1.369 (6) | C25—H25A | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C26—C27 | 1.358 (6) |
| C7—C8 | 1.405 (5) | C26—H26A | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9300 | C27—C28 | 1.380 (6) |
| C9—C10 | 1.457 (5) | C28—C29 | 1.380 (5) |
| C11—C12 | 1.467 (6) | C28—H28A | 0.9300 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | ||
| C8—N1—C9 | 109.6 (3) | C14—C13—C1 | 129.2 (3) |
| C8—N1—H1A | 125.2 | C15—C14—C19 | 117.7 (3) |
| C9—N1—H1A | 125.2 | C15—C14—C13 | 135.6 (3) |
| C2—C1—C24 | 111.6 (3) | C19—C14—C13 | 106.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C13 | 113.6 (3) | C16—C15—C14 | 118.8 (4) |
| C24—C1—C13 | 113.4 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 120.6 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 105.8 | C14—C15—H15A | 120.6 |
| C24—C1—H1B | 105.8 | C15—C16—C17 | 121.7 (4) |
| C13—C1—H1B | 105.8 | C15—C16—H16A | 119.1 |
| C10—O2—C11 | 118.2 (3) | C17—C16—H16A | 119.1 |
| C19—N2—C20 | 109.6 (3) | C18—C17—C16 | 121.4 (4) |
| C19—N2—H2A | 125.2 | C18—C17—H17A | 119.3 |
| C20—N2—H2A | 125.2 | C16—C17—H17A | 119.3 |
| C9—C2—C3 | 105.7 (3) | C17—C18—C19 | 117.9 (4) |
| C9—C2—C1 | 125.0 (3) | C17—C18—H18A | 121.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 129.3 (3) | C19—C18—H18A | 121.0 |
| C21—O3—C22 | 115.8 (3) | N2—C19—C18 | 129.6 (3) |
| C4—C3—C8 | 117.6 (3) | N2—C19—C14 | 108.0 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 135.5 (3) | C18—C19—C14 | 122.5 (3) |
| C8—C3—C2 | 106.9 (3) | N2—C20—C13 | 109.0 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.1 (4) | N2—C20—C21 | 117.0 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.5 | C13—C20—C21 | 134.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.5 | O4—C21—O3 | 122.9 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.2 (4) | O4—C21—C20 | 123.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 118.9 | O3—C21—C20 | 113.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 118.9 | O3—C22—C23 | 107.4 (4) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.2 (4) | O3—C22—H22A | 110.2 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 119.4 | C23—C22—H22A | 110.2 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.4 | O3—C22—H22B | 110.2 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 117.2 (4) | C23—C22—H22B | 110.2 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 121.4 | H22A—C22—H22B | 108.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 121.4 | C22—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—C7 | 129.0 (3) | C22—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—C3 | 108.2 (3) | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C3 | 122.8 (4) | C22—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| N1—C9—C2 | 109.6 (3) | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| N1—C9—C10 | 118.8 (3) | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C2—C9—C10 | 131.6 (3) | C25—C24—C29 | 116.6 (3) |
| O1—C10—O2 | 123.8 (3) | C25—C24—C1 | 123.2 (3) |
| O1—C10—C9 | 122.4 (3) | C29—C24—C1 | 120.2 (3) |
| O2—C10—C9 | 113.7 (3) | C26—C25—C24 | 121.2 (4) |
| O2—C11—C12 | 107.0 (3) | C26—C25—H25A | 119.4 |
| O2—C11—H11A | 110.3 | C24—C25—H25A | 119.4 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 110.3 | C27—C26—C25 | 120.0 (4) |
| O2—C11—H11B | 110.3 | C27—C26—H26A | 120.0 |
| C12—C11—H11B | 110.3 | C25—C26—H26A | 120.0 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 108.6 | C26—C27—C28 | 121.3 (4) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C26—C27—Cl1 | 120.4 (4) |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C28—C27—Cl1 | 118.3 (3) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C29—C28—C27 | 118.0 (4) |
| C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C29—C28—H28A | 121.0 |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C27—C28—H28A | 121.0 |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C28—C29—C24 | 122.9 (4) |
| C20—C13—C14 | 106.8 (3) | C28—C29—Cl2 | 118.1 (3) |
| C20—C13—C1 | 124.0 (3) | C24—C29—Cl2 | 119.0 (3) |
| C24—C1—C2—C9 | −156.0 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 178.9 (4) |
| C13—C1—C2—C9 | 74.3 (4) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.6 (7) |
| C24—C1—C2—C3 | 23.5 (5) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 1.1 (8) |
| C13—C1—C2—C3 | −106.2 (4) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −1.1 (8) |
| C9—C2—C3—C4 | 178.7 (4) | C20—N2—C19—C18 | 179.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.9 (7) | C20—N2—C19—C14 | −0.5 (4) |
| C9—C2—C3—C8 | 0.3 (4) | C17—C18—C19—N2 | −179.2 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C8 | −179.3 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | 0.7 (7) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 1.4 (6) | C15—C14—C19—N2 | 179.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −176.9 (4) | C13—C14—C19—N2 | 0.6 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (7) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | −0.3 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.6 (7) | C13—C14—C19—C18 | −179.4 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.7 (6) | C19—N2—C20—C13 | 0.2 (4) |
| C9—N1—C8—C7 | −176.9 (4) | C19—N2—C20—C21 | −178.2 (3) |
| C9—N1—C8—C3 | 1.5 (4) | C14—C13—C20—N2 | 0.1 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—N1 | 178.5 (4) | C1—C13—C20—N2 | 179.2 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C3 | 0.3 (6) | C14—C13—C20—C21 | 178.2 (4) |
| C4—C3—C8—N1 | −179.8 (3) | C1—C13—C20—C21 | −2.7 (6) |
| C2—C3—C8—N1 | −1.1 (4) | C22—O3—C21—O4 | 0.0 (5) |
| C4—C3—C8—C7 | −1.3 (5) | C22—O3—C21—C20 | 180.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C8—C7 | 177.5 (3) | N2—C20—C21—O4 | 4.9 (5) |
| C8—N1—C9—C2 | −1.4 (4) | C13—C20—C21—O4 | −173.1 (4) |
| C8—N1—C9—C10 | 176.0 (3) | N2—C20—C21—O3 | −175.1 (3) |
| C3—C2—C9—N1 | 0.6 (4) | C13—C20—C21—O3 | 7.0 (6) |
| C1—C2—C9—N1 | −179.7 (3) | C21—O3—C22—C23 | −179.8 (4) |
| C3—C2—C9—C10 | −176.2 (3) | C2—C1—C24—C25 | −110.9 (4) |
| C1—C2—C9—C10 | 3.4 (6) | C13—C1—C24—C25 | 18.9 (5) |
| C11—O2—C10—O1 | −4.5 (5) | C2—C1—C24—C29 | 69.4 (4) |
| C11—O2—C10—C9 | 173.4 (3) | C13—C1—C24—C29 | −160.8 (3) |
| N1—C9—C10—O1 | 3.8 (5) | C29—C24—C25—C26 | −2.0 (5) |
| C2—C9—C10—O1 | −179.5 (4) | C1—C24—C25—C26 | 178.3 (3) |
| N1—C9—C10—O2 | −174.1 (3) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 0.0 (6) |
| C2—C9—C10—O2 | 2.5 (5) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | 1.5 (6) |
| C10—O2—C11—C12 | −167.2 (3) | C25—C26—C27—Cl1 | −178.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C13—C20 | −162.4 (3) | C26—C27—C28—C29 | −0.9 (7) |
| C24—C1—C13—C20 | 68.8 (4) | Cl1—C27—C28—C29 | 179.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C13—C14 | 16.4 (5) | C27—C28—C29—C24 | −1.2 (7) |
| C24—C1—C13—C14 | −112.3 (4) | C27—C28—C29—Cl2 | −179.8 (3) |
| C20—C13—C14—C15 | −179.2 (4) | C25—C24—C29—C28 | 2.6 (6) |
| C1—C13—C14—C15 | 1.8 (7) | C1—C24—C29—C28 | −177.7 (4) |
| C20—C13—C14—C19 | −0.4 (4) | C25—C24—C29—Cl2 | −178.8 (3) |
| C1—C13—C14—C19 | −179.4 (3) | C1—C24—C29—Cl2 | 0.9 (5) |
| C19—C14—C15—C16 | 0.2 (6) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg5 are the centroids of the N1,C8,C3,C2,C9 and C24–C29 rings respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1i | 0.86 | 2.07 | 2.864 (4) | 152 |
| N2—H2A···O4ii | 0.86 | 2.04 | 2.871 (4) | 161 |
| C11—H11A···Cl1iii | 0.97 | 2.81 | 3.731 (5) | 158 |
| C4—H4A···Cg5 | 0.93 | 2.77 | 3.516 (4) | 137 |
| C15—H15A···Cg1 | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.476 (5) | 139 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, −z; (iii) x−1, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by University of Natural Science Foundation in Jiangsu Province grant 17KJB320001. Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions grant PPZY2015B179. Training program of Students innovation and entrepreneurship in Jiangsu Province grant 201712920001Y. Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province grant .
References
- Chang, Y.-C., Riby, J., Chang, G. H., Peng, G.-F., Firestone, G. & Bjeldanes, L. F. (1999). Biochem. Pharmacol. 58, 825–834. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Enraf–Nonius (1994). CAD-4 EXPRESS. Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Ge, X., Fares, F. A. & Yannai, S. (1999). Anticancer Res. 19, 3199–3203. [PubMed]
- Harms, K. & Wocadlo, S. (1995). XCAD4. University of Marburg, Germany.
- Li, Y., Sun, H., Jiang, H., Xu, N. & Xu, H. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, 259–261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.-H., Sun, H.-S. & Hu, J. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, 593–595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Ni, Y.-C. (2008). Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 4, 96–112.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Porter, J. K., Bacon, C. W., Robbins, J. D., Himmelsbach, D. S. & Higman, H. C. (1977). J. Agric. Food Chem. 25, 88–93. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-S., Li, Y., Jiang, H., Xu, N. & Xu, H. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 1140–1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-S., Li, Y.-L., Xu, N., Xu, H. & Zhang, J.-D. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, R. J. (1996). The Chemistry of Indoles, p. 113 New York: Academic Press.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017015730/sj5539sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017015730/sj5539Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017015730/sj5539Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1582719
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




