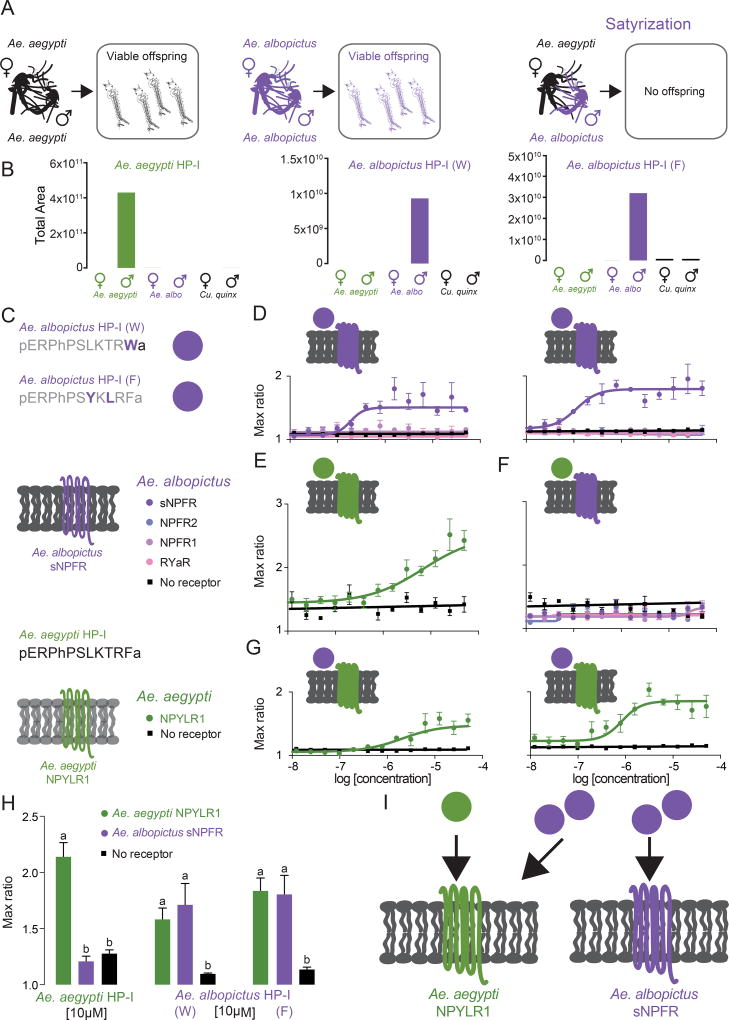
Fig 4. Ae. albopictus HP-I Peptides are Potent Activators of Ae. aegypti NPYLR1.
(A) Schematic of normal within-species mating (left and middle) and cross-species satyrization of Ae. aegypti females by Ae. albopictus males (right).
(B) Relative levels of mature Aedes aegypti HP-I and Aedes albopictus HP-I RWamide and RFamide peptides detected by LC-MS in whole adult mosquitoes of the indicated sex and species.
(C) Legend for cell-based assay experiments in C–G, including the amino acid sequences of predicted mature HP-I in Ae. albopictus compared to Ae. aegypti HP-I.
(D) Dose-response curves of Ae. albopictus HP-I peptides (W and F) on Ae. albopictus receptors.
(E) Dose-response curve of Ae. aegypti HP-I on Ae. aegypti NPYLR1.
(F) Dose-response curves of Ae. aegypti HP-I on Ae. albopictus neuropeptide receptors.
(G) Dose-response curves of Ae. albopictus HP-I peptides (W and F) on Ae. aegypti NPYLR1.
(H) Responses to 10µM Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus HP-I peptides. Data in C–G are shown as max ratio (maximum fluorescence level/baseline fluorescence level) (mean ± SEM, 3 replicates. *** p < 0.0001, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test).
(I) Schematic of activity of Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus HP-I peptides against Ae. aegypti NPYLR1 and Ae. albopictus sNPFR.