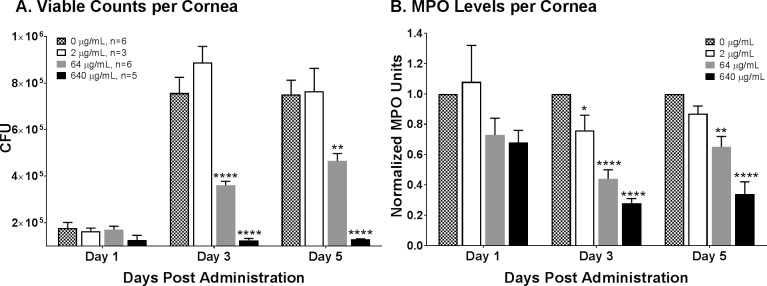
Figure 8.
RP444 topical treatment reduces bacterial load and inflammatory cell infiltration in a murine P. aeruginosa keratitis model. (A) Viable bacterial counts in infected corneas treated with RP444 at 64 and 640 μg/mL were significantly lower than in PBS-treated animals at days 3 and 5 post infection. (B) A dose-dependent decrease in inflammatory cell infiltration, as measured by myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, was observed in RP444-treated animals at days 3 and 5 post infection. Data are from three to six independent samples generated in one (2 and 640 μg/mL) or two experiments (64 μg/mL). Statistical significance was *P < 0.5, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.