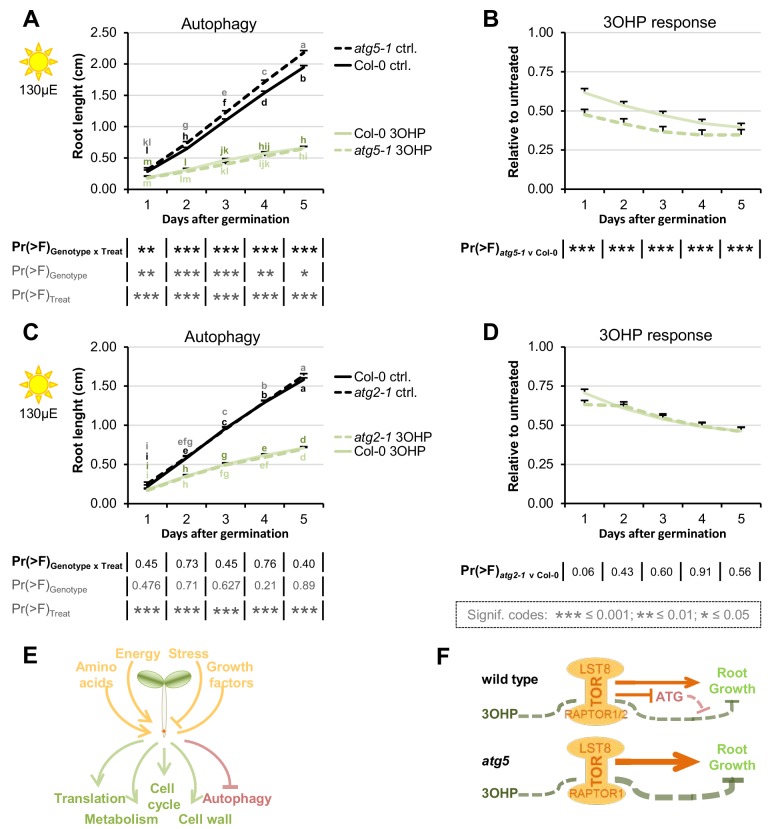
Figure 8. Blocking autophagosome elongation amplifies the 3OHP response.
(A) Root growth for atg5-1 and wildtype Col-0 seedlings grown on MS medium supplemented with or without 5 µM 3OHP. Multi-factorial ANOVA was used to test the impact of Genotype (Col-0 v atg5-1), Treatment (Control v 3OHP) and their interaction on root length. All experiments were combined in the model and experiment treated as a random effect. The ANOVA results from each day are presented in the table. (B) Root lengths in response to 3OHP (from A) displayed at each time point as relative to untreated. Results are least squared means ± SE over two independent experimental replicates with each experiment having an average of 21 replicates per condition (n = 31–52). (C) Root growth for atg2-1 and wildtype Col-0 seedlings grown on MS medium supplemented with or without 5 µM 3OHP. Multi-factorial ANOVA was used to test the impact of Genotype (Col-0 v atg5-1), Treatment (Control v 3OHP) and their interaction on root length. All experiments were combined in the model and experiment treated as a random effect. The ANOVA results from each day are presented in the table. (D) Root lengths in response to 3OHP treatment (from C) displayed at each time point as relative to untreated. Results are least squared means ± SE over two independent experimental replicates with each experiment having an average of 26 replicates per condition (n = 36–66). (E) The TOR complex (TORC), is affected by several upstream input, leading to activation or repression of several downstream pathways. (F) Schematic model; sucrose activates TORC, leading to root growth. 3OHP represses root growth through interaction with TORC. Autophagy pathways via ATG5 negatively affect 3OHP response.