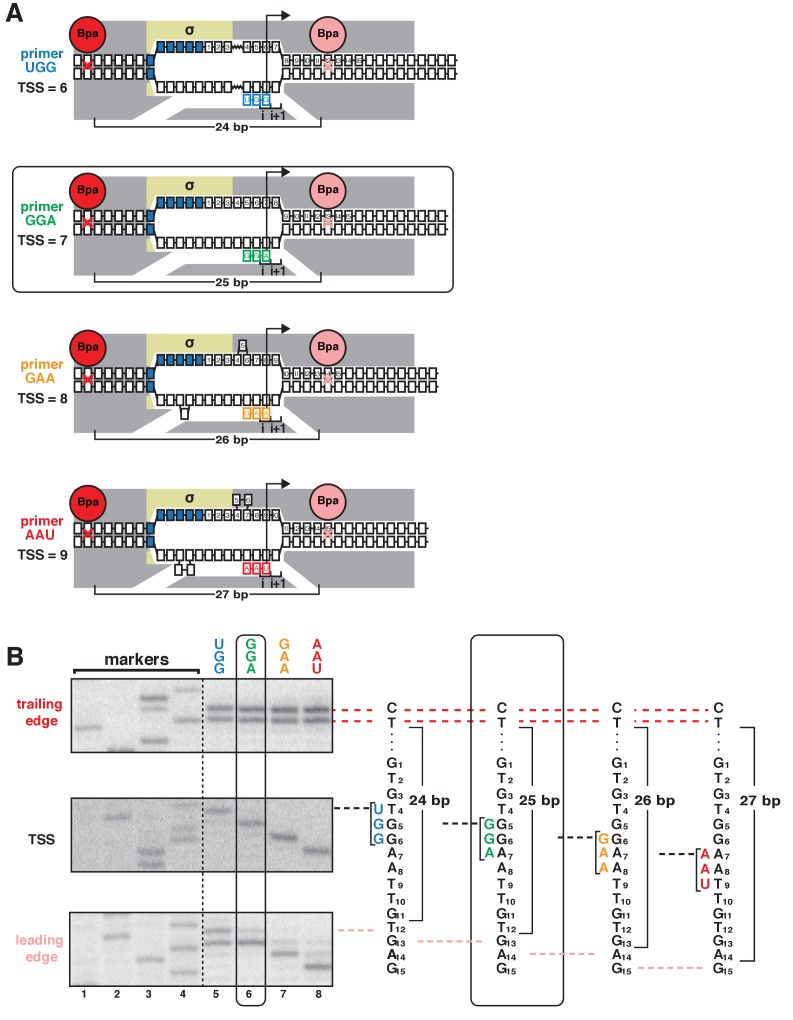
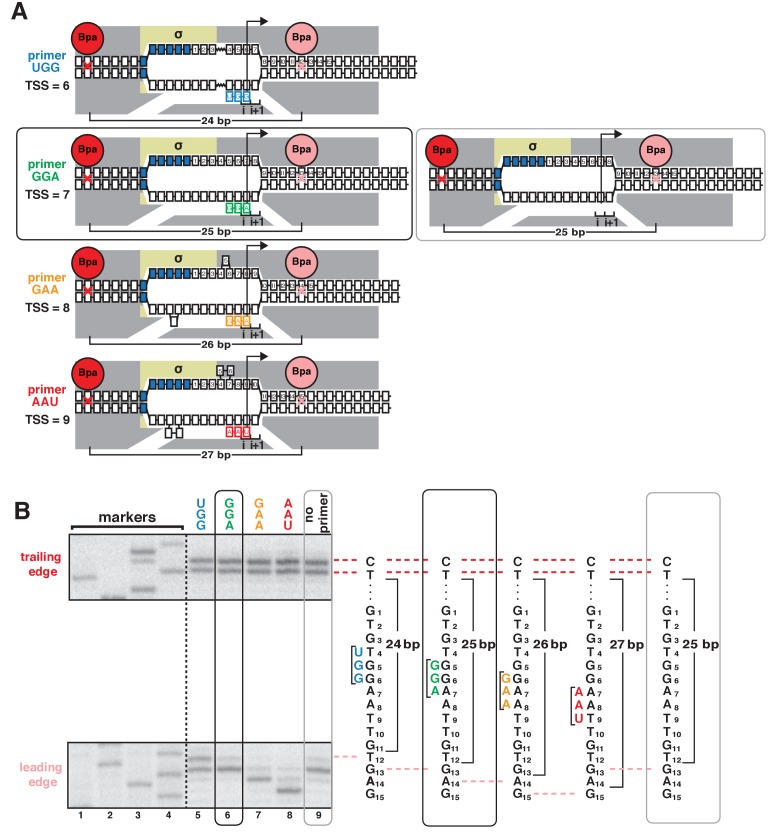
Figure 3. TSS selection downstream and upstream of the modal TSS involves, respectively, forward and reverse movements of RNAP leading edge.
(A) Ribotrinucleotide primers program TSS selection at positions 6, 7, 8, and 9 bp downstream of −10 element (UGG, GGA, GAA, and AAU). Cyan, green, orange, and red denote primers UGG, GGA, GAA, and AAU, respectively. Rectangle with rounded corners highlights case of primer GGA, which programs TSS selection at same position as in absence of primer (7 bp downstream of −10 element). Other colors as in Figure 1A. (B) Use of protein-DNA photocrosslinking to define RNAP leading-edge and trailing-edge positions in vitro. RNAP trailing-edge crosslinking (top), TSS (middle), and RNAP leading-edge crosslinking (bottom) with primers UGG, GGA, GAA, and AAU (lanes 5–8). Horizontal dashed lines relate bands on gel (left) to nucleotide sequences (right).