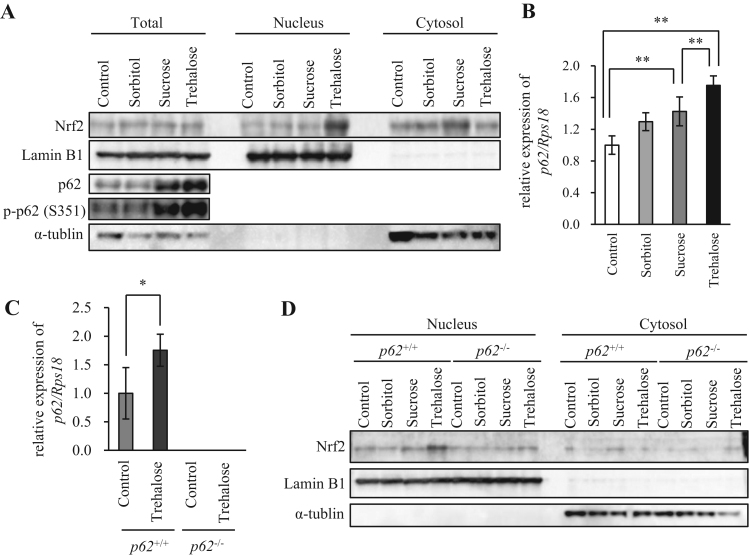
Fig. 3.
Trehalose enhanced the effects of p62 expression and promoted Nrf2 nuclear translocation. (A) Hepa1-6 cells were treated with 50 mM sorbitol, sucrose or trehalose for 24 h, while untreated cells were used as a control. Total, nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting using anti-Nrf2, p62, p-p62 (S351), LaminB1 and α-tubulin antibodies. LaminB1 and α-tubulin were used as the loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts, respectively. (B) Hepa1-6 cells were treated with 50 mM sorbitol, sucrose, or trehalose for 24 h and harvested, while untreated cells were used as a control. p62 mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR (n = 4). Data were normalized against Rps18 expression (n = 4). Values are means ± SD. Differences among values were analyzed by the Tukey-Kramer method with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (C) p62+/+ or p62-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were treated with 50 mM trehalose for 24 h and harvested. Expression of p62 mRNA was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR (n = 4). Data were normalized against Rps18 (n = 4). Values are means ± SD. Differences between values were analyzed by Student's t-test. Statistical significance shown as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (D) p62+/+ or p62-/- MEFs were treated with 50 mM sorbitol, sucrose or trehalose for 24 h. Untreated cells were used as a control. Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting using anti-Nrf2, LaminB1 and α-tubulin antibodies. LaminB1 and α-tubulin were used as the loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts, respectively. Data are representative of two independent experiments.