Figure 4.
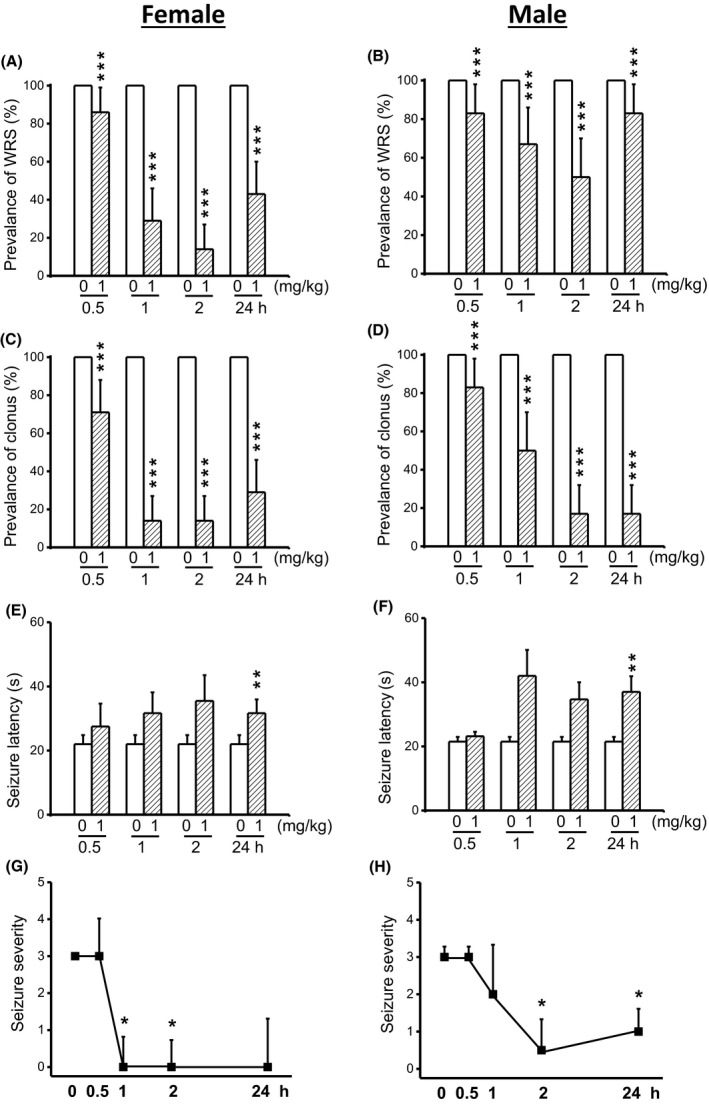
Effects of semichronic CPZ treatment on the expression of acoustically seizure susceptibility in GEPR‐3s. The effects of CPZ at a dose of 1 mg/kg (ip) were evaluated on the prevalence and severity of seizures in both female (n = 6) and male (n = 6) GEPR‐3s at different time points of 0.5, 1, 2, and 24 h. CPZ at a dose of 1 mg/kg (ip) markedly reduced the prevalence of WRS in female (panel A) and male (panel B) GEPR‐3s. CPZ treatment also reduced the prevalence of clonus in female (panel C) and male (panel D) GEPR‐3s. The anticonvulsant effect was associated with increased seizures latency in female (panel E) and male (panel F) GEPR‐3s. Time course of the effects of CPZ treatment showed a long‐lasting complete seizure suppression by the 1st hour posttreatment in female GEPR‐3s (panel G). In male GEPR‐3s, CPZ reduced the seizure severity by the 2nd hour posttreatment (panel H). The prevalence of WRS and clonus, seizure latency, and seizure severity was analyzed as described in Figure 1. Opened and filled bar graphs represent controls (pre‐CPZ) and CPZ‐treated GEPR‐3s, respectively. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
