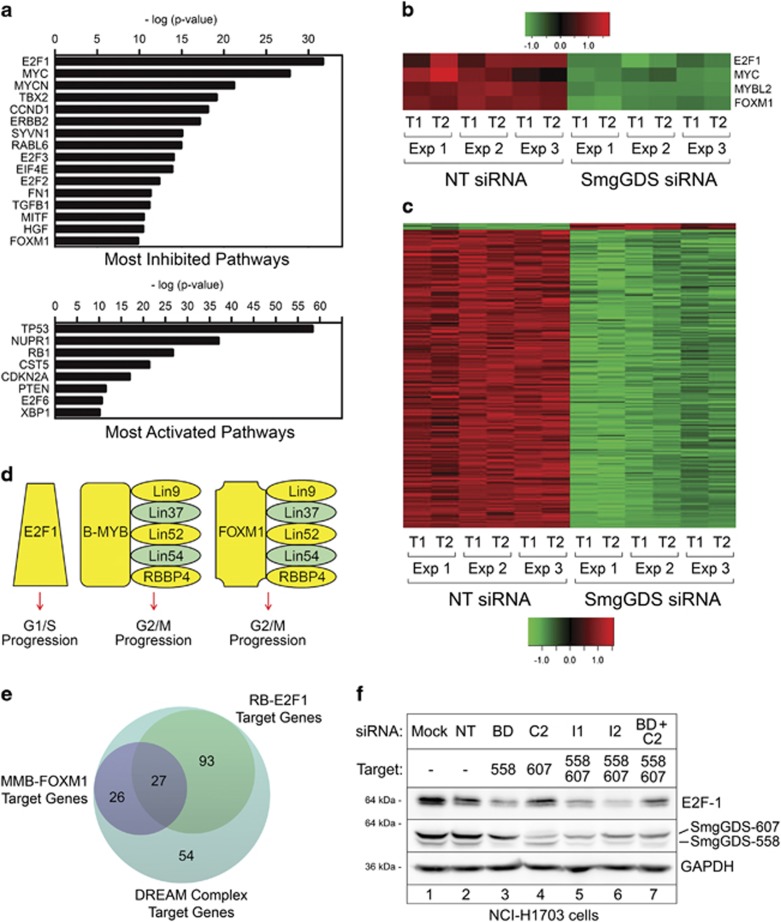
Figure 1.
Depletion of SmgGDS diminishes expression of DREAM complex target genes required for cell cycle progression. (a) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of microarray data from NCI-H1703 cells depleted of both SmgGDS-558 and SmgGDS-607 using siRNA I1 shows significant effects on gene expression within the indicated pathways. (b, c) Heatmaps display changes in expression of the 200 DREAM target genes that were most significantly altered in NCI-H1703 cells treated with siRNA I1, generated in two technical replicates (T1 and T2) from three independent experiments (Exp 1, 2 and 3). (d) Protein complexes containing E2F1, B-MYB, FOXM1 and Lin family members promote cell cycle progression, and yellow highlights identify specific gene products that exhibit reduced expression in NCI-H1703 cells following depletion of SmgGDS with siRNA I1. (e) The 200 DREAM target genes that were most significantly altered in SmgGDS-depleted cells (shown in c) were analyzed using the targetgenereg.org24 database to predict which of these target genes are regulated by Rb-E2F1 or MMB-FOXM1 complexes. (f) Immunoblotting was used to examine E2F1 protein expression in NCI-H1703 cells following depletion of different SmgGDS isoforms using specific siRNAs (n=3). Mean normalized densitometry values are shown in Supplementary Figure S1b.