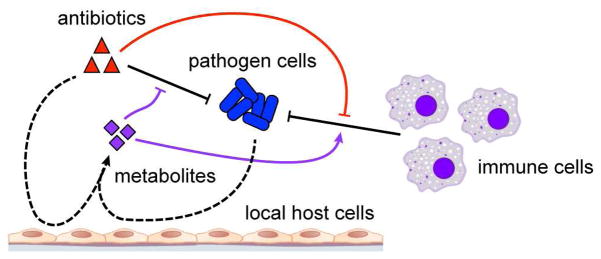
Figure 6. Metabolic effects of antibiotic treatment on host cells inhibit drug efficacy and impair immune function.
During infection, antibiotics work in concert with immune cells to clear microbial pathogens (black). Meanwhile, antibiotics and pathogen cells metabolically remodel the local infectious microenvironment by acting on local host cells (dashed). Induced metabolites can inhibit drug efficacy and potentiate immune function (purple). Direct actions by antibiotics on immune cell metabolism can also impair immune cell phagocytic activity (red).