Fig. 5. Analysis of the involvement of IL13 receptors in regulation of tricellulin and claudin 2.
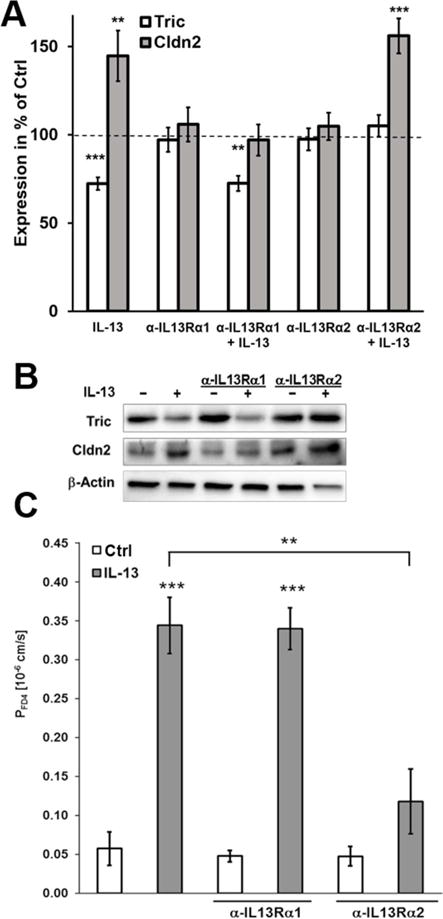
A. Densitometric analysis of protein expression of HT-29/B6 cells treated with inhibitory antibodies and IL-13. In HT-29/B6, the inhibitory antibody against IL13 receptor α1 is able to inhibit the IL-13-caused increase of claudin-2, but not the decrease of tricellulin. Tricellulin decrease by IL-13 is inhibited by blocking the IL-13 receptor α 2, while its inhibition has no effect on the claudin-2 increase (n=7–11). B. Representative western blots of the incubation with inhibitory antibodies and IL-13. C. Permeability for 4 kDa-FITC dextran. Permeability for FD4 is increased in HT-29/B6 cells treated with IL-13. This effect was not inhibited by preincubation with the inhibitory antibody against IL13 receptor α1, but was abolished by preincubation with the inhibitory antibody against IL13 receptor α2 (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001, n=4).
