Fig. 7. Analysis of the signaling pathways regulating tricellulin and claudin 2.
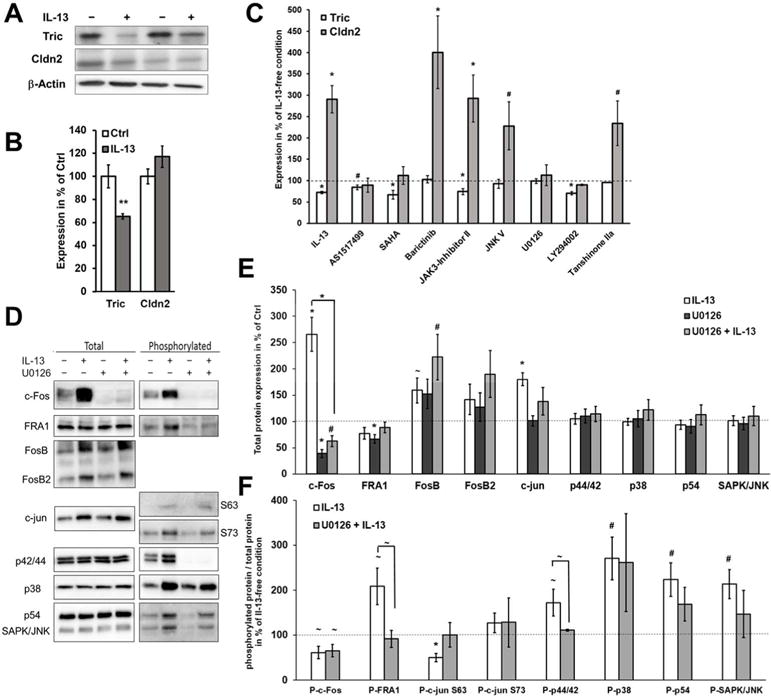
A. Representative western blots of STAT6−/− mice treated with IL-13. IL-13 treatment still decreases tricellulin, while claudin-2 expression is at levels of untreated mice due to absence of STAT6 (n=4–6). B. Densitometric analysis of protein expression in colon tissue of untreated and IL-13-treated STAT6−/− mice. After treatment, tricellulin is decreased (**p<0.01), while claudin-2 is unaffected. C. Densitometric analysis of protein expression of HT-29/B6 pretreated with different inhibitors before application of IL-13 (representative blots see Fig. S6, n=4–12). Protein expression levels were normalized to the respective inhibitor treatment without IL-13. Inhibitors targeting STAT6, ERK1/2, MAPK, and PI3K affect the IL-13-caused increase of claudin-2, while inhibitors targeting JAK1 and/or JAK2, JNK, ERK1/2, MAPK and AP-1 inhibit the IL-13-caused decrease of tricellulin (#p<0.05; *p<0.01, n=6–12). D. Representative western blots of total and phosphorylated proteins involved in ERK1/2 and AP-1 signaling. HT-29/B6 cells are either pretreated or not with U0126 before application of IL-13. E. Densitometric analysis of total protein. Expression of cFos, FosB and c-jun is increased by IL-13 (*p<0.001, #p<0.01, ~p<0.05; n=12). U0126 inhibits this increase for c-Fos (IL-13: 265±33%, ***p<0.001; U0126+IL-13: 63±11 %, ***p<0.001 to IL-13). F. Ratio of phosphorylated protein to total protein under influence of IL-13. Phosphorylation levels are increased by IL-13 for FRA-1, p44/42, p38, p54 and SAPK/JNK and decreased for c-Fos and c-jun (S63; IL-13: 50±10%, ***p<0.001; U0126+IL-13: 92±18 %, *p<0.05 to IL-13, n=12). These changes in phosphorylation are inhibited by U0126 only for FRA-1 (IL-13: 209±41%, *p<0.05; U0126 + IL-13: 92±19 %, *p<0.05 to IL-13, n=12) and p44/42 (ERK1/2; IL-13: 173±30%, *p<0.05; U0126+IL-13: 6±2 %, *p<0.05 to IL-13, n=12) (n=10–12).
