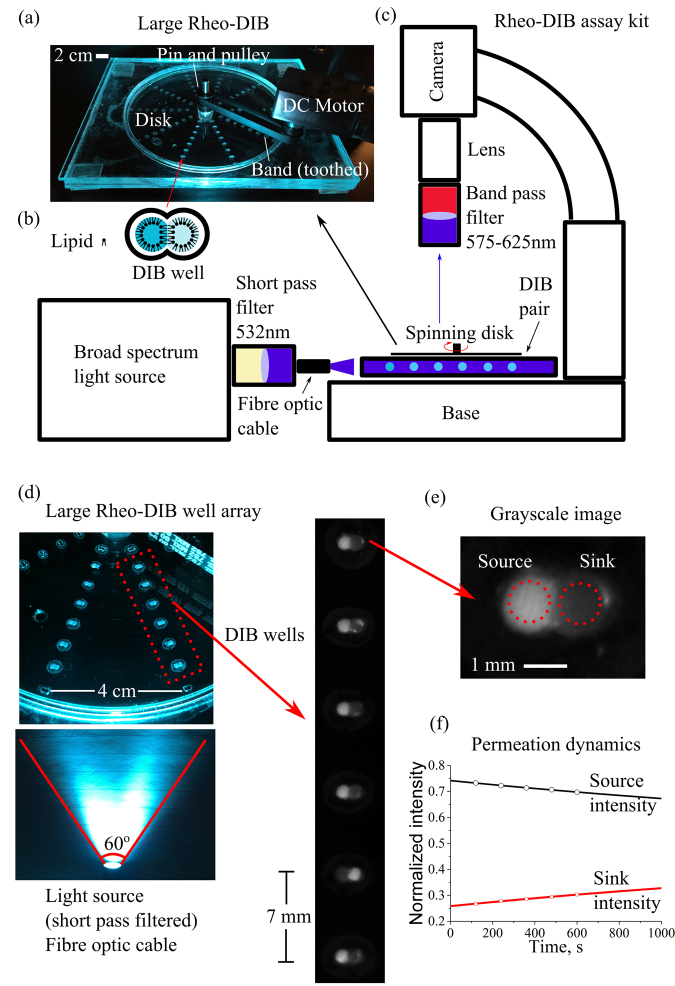
Figure 5.
Photograph (a) of the large rheo-DIB device for an expanded permeation assay, where 10 columns of 8 DIB wells (b) are arrayed around the device centre. The device is driven by a DC brushed motor and variable power supply (20 volts) that is connected to a pulley gear via a toothed band. Schematic (c) of the bespoke assay kit consists of an Olympus stereoscope stand with a non-reflective base where the device is mounted below a microscope camera fitted with a macro lens and band pass filters (575–624 nm). The device is illuminated with a broad spectrum light source where the output is filtered by a short pass filter (532 nm). To ensure a uniform illumination, the fibre optic cable position can be adjusted to optimize intensity distribution. Photograph (d) of the large rheo-DIB device, where the filtered light illuminates the fluorescent DIBs, which are viewed as micrograph images of the DIB columns. The dynamic intensity of the grayscale DIB images (e) are used to measure the permeation dynamics (f), which, along with the droplet volume and DIB contact area, are fit to Fick’s 1st law of diffusion.