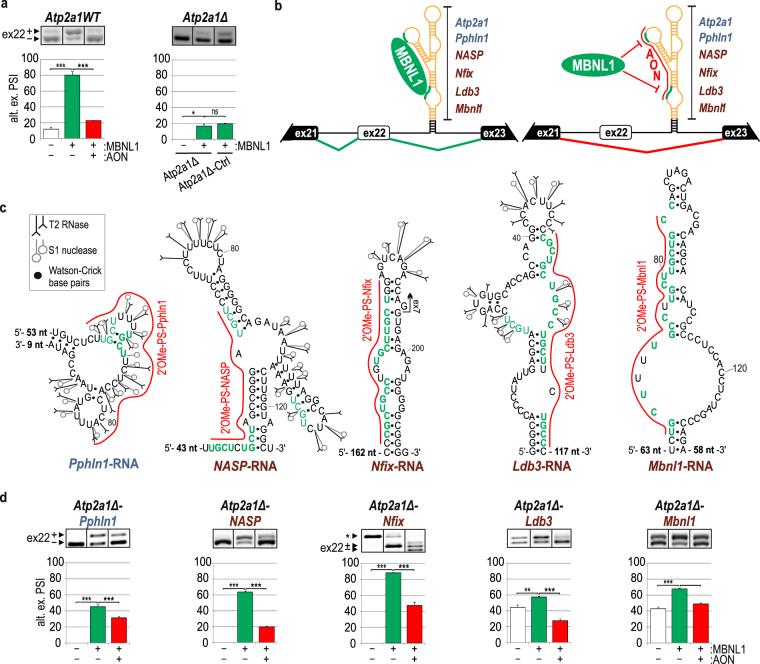
Figure 3.
Hybrid Atp2a1 minigenes confirm the functional intronic and exonic MBNL-binding regions. (a) Percentage of alternative ex22 inclusion in Atp2a1WT and Atp2a1Δ mRNA, lacking a fragment containing MBNL-binding regions, upon MBNL1 overexpression with or without 2′OMe-PS (AON) treatment; n = 3. Atp2a1Δ-Ctrl, a hybrid minigene with an inserted control sequence cassette lacking MBNL-binding regions; n = 2. (b) The schemes illustrate a general organization of hybrid Atp2a1 minigenes containing an MBNL-responsive cassette derived from analyzed transcripts in the place of a natural Atp2a1 cassette within intron 22. We expect to observe the promotion of ex22 through MBNLs binding to YGCY sequence motifs within inserted cassettes (green line) and ex22 exclusion upon AONs blocking MBNL-binding regions (red line). A thermodynamically stable structure having 14-nt-long complementary sequences derived from intron 22, restriction sites and 5-bp artificial helix, is marked with black. It is distant by 32–164 nucleotides from the MBNL-binding sites. (c) Experimentally determined secondary structures of selected areas of analyzed short intronic and exonic RNA fragments containing significant MBNL-binding regions complementary to specific AONs and marked with a red line. The entire structures of the analyzed in vitro RNA fragments are presented in Supplementary Fig. S4b. The number of not shown nucleotides is depicted on the 5′ and/or 3′ end of each structure. YGCY motifs are marked with green and in bold if present in humans and mice. Mbnl1-RNA was previously described38. (d) Percentage of alternative ex22 inclusion in the mRNA of a set of hybrid Atp2a1 minigenes upon MBNL1 overexpression with or without treatment with specific 2′OMe-PS AONs. The asterisk indicates an artificial splicing isoform of the Atp2a1Δ-Nfix minigene; n = 3.