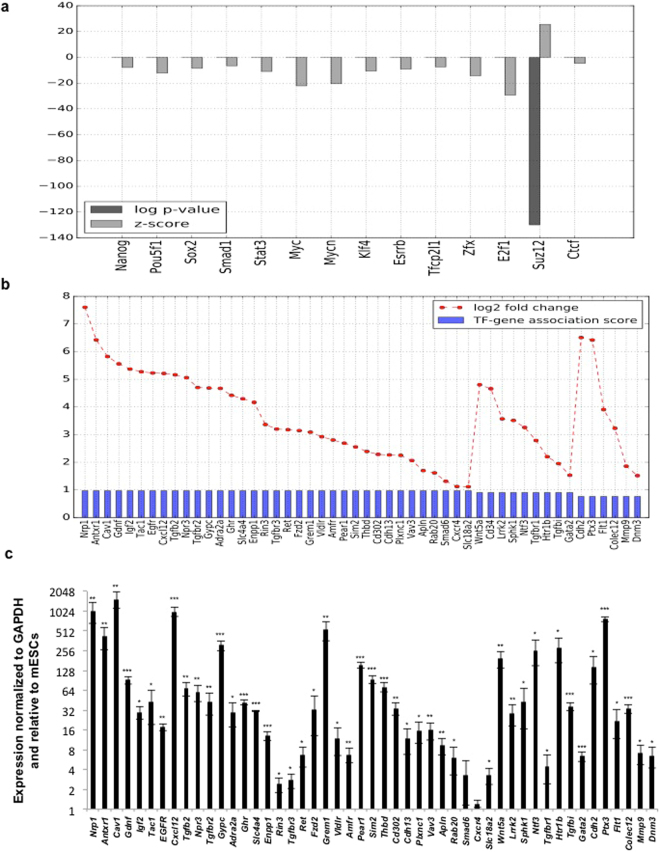
Figure 1.
In silico identification of transcription factors and transcriptional regulators that regulate endocytic gene expression in pluripotent and differentiated cells. (a) Bar chart displaying the statistical association between gene sets bound by different transcriptional regulators (from ChIP-seq binding data in Chen et al.), and the set of genes whose expression levels are 2-fold higher in MEFs relative to mESCs. Differentially upregulated genes are significantly over-represented in the gene targets of SUZ12 (indicated by a low p-value and high Z-score). (b) Bar chart showing the 50 genes with known association with endocytosis, whose promoter regions are bound by SUZ12 and are upregulated in MEFs relative to mESCs. The interaction score between SUZ12 and each gene, as well as the log2 fold expression change of each gene, are shown. (c) RT-qPCR analysis of SUZ12 bound endocytic genes in mESCs and MEFs. mRNA expression is normalized to Gapdh, and further normalized to expression in mESCs. Error bars represent mean ± S.D for experiments in triplicates (N = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 by Students T-test.