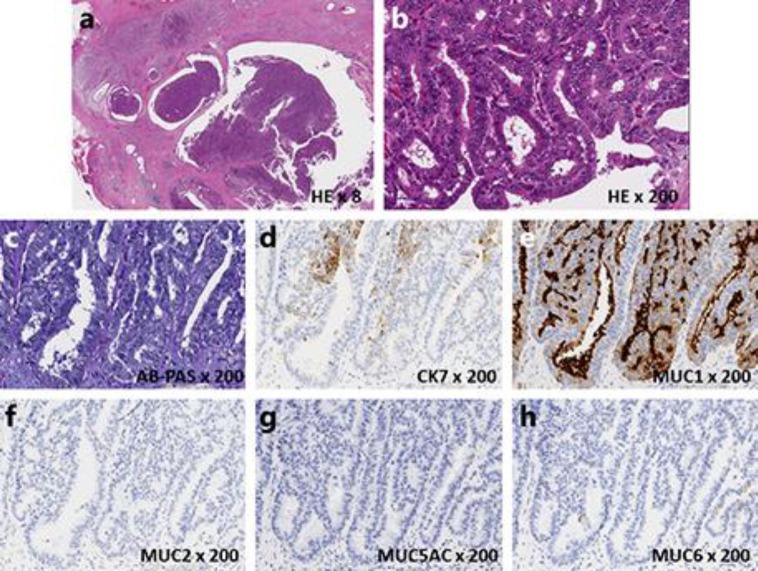
Fig. 3.
a A low-magnification image showing an intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm. Not only the main pancreatic duct but also the branches of the pancreatic ducts were replete with tumor cells. b A high-magnification image revealed that the tumor was composed of solid proliferating tumor cells with tubular or papillary formation with high-grade dysplasia. c There was no mucin that was detectable by AB-PAS stain. d–h An immunohistochemical examination revealed that the tumor cells were positive for CK7 and MUC1, but negative for MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6.