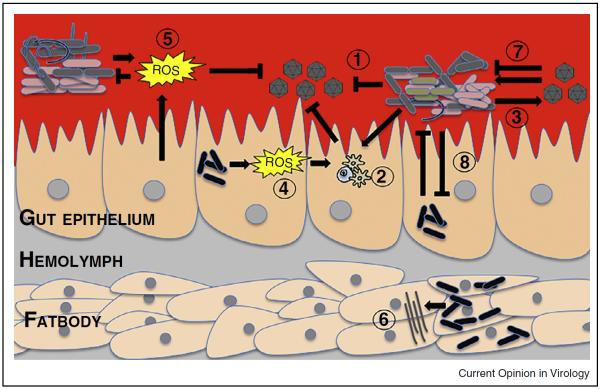
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrating the tripartite interactions between the mosquito host, the microbiome and arboviruses. Members of the microbiome can directly impede viruses (1), or can stimulate basal immunity leading to virus suppression (2). Conversely, some bacterial species can enhance viruses (3). Intracellular bacteria such as Wolbachia can also stimulate immunity by production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (4). ROS can also be generated by the mosquito host and members of the microbiome and suppresses bacteria and pathogens (5). Intracellular bacteria can also manipulate host miRNA expression (6). Arboviruses can both suppress and enhance members of the microbiome (7) while bacterial interactions also influence the microbiome composition (8).