Fig. 2. Regulation of Tat-dependent HIV-1 transcription. 1) ZASC1 recruits the 7SK snRNP to the 5′LTR in a TAR-independent manner.
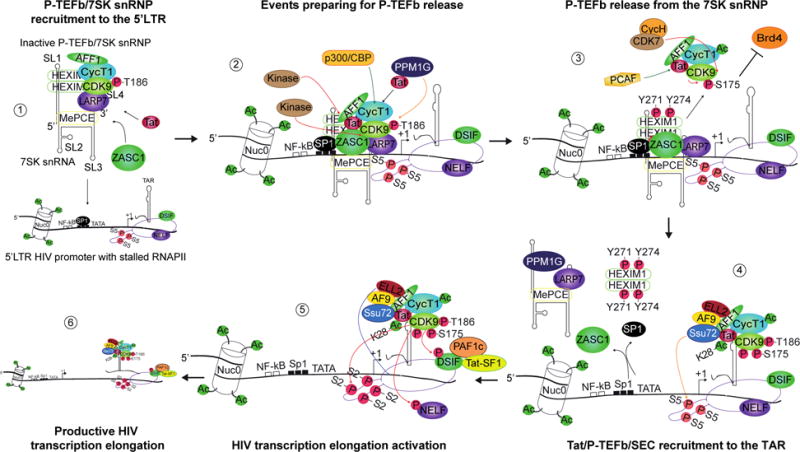
Tat binds to P-TEFb within the 7SK snRNP. ZASC1 binds to Tat and recruits the 7SK snRNP to the 5′LTR by binding two overlapping antiparallel binding sites immediately downstream of the TATA-box with a possible cooperative role of Sp1. 2) Events facilitating P-TEFb release from the 7SK snRNP. Tat competes HEXIM1 to bind P-TEFb and release it from the inhibitory 7SK snRNP complex, assisted by the scaffolding protein AFF1, which mediates an increase in Tat/CycT1 affinity for P-TEFb and by several coordinated PTMs of Tat, P-TEFb and HEXIM1. p300/CBP acetylates several residues within CycT1, a necessary step for P-TEFb release. A still uncharacterized kinase phosphorylates Tyr271 and Tyr274 on HEXIM1 facilitating 7SK snRNP dissociation. Phosphorylation of CDK9 Ser175 is also detrimental to the HEXIM1/P-TEFb interaction. Moreover, Tat recruits the phosphatase PPM1G to 7SK snRNP, which dephosphorylates CDK9 Thr186 leading to HEXIM1/P-TEFb dissociation and P-TEFb/Tat exit from the 7SK snRNP complex. 3) Tat/Brd4 competition for P-TEFb release from 7SK snRNP. Phosphorylated CDK9 at Ser175 favors Tat competition with Brd4 for P-TEFb binding, by increasing or decreasing their CDK9 affinity respectively and hence favors the formation of AFF1/Tat/P-TEFb over AFF1/Brd4/P-TEFb. Acetylation of Tat Lys28 is also important for TMT. Tat may be acetylated by PCAF within the 7SK snRNP complex or after Tat/P-TEFb release, a critical step in Tat-mediated P-TEFb recruitment to the TAR. The required CDK9 phosphorylation by CDK7/CycH at Thr186 is potentiated by Tat in complex with P-TEFb and the SEC subunit AFF1. Autophosphorylation of several Ser/Thr in the CDK9 C-terminus is required for Tat/P-TEFb association to TAR 4) SEC/Tat/TAR/P-TEFb association and role of Ssu72 in RNAPII-mediated transcription elongation. Following phosphorylation, HEXIM1 dissociates from 7SK snRNP and both release the 5′LTR. Active P-TEFb, is recruited by Tat to TAR, in complex with the complete AFF1/ELL2/AF9 SEC near the stalled RNAPII. Ssu72 is recruited by Tat and dephosphorylates RNAPII CTD Ser5. 5) CDK9 phosphorylates RNAPII and the negative elongation factors. CDK9 mediates Ser2 phosphorylation of the heptapeptide of the RNAPII CTD to activate transcription elongation. The negative factor DSIF is also phosphorylated by CDK9 becoming a positive elongation factor. PAF1c and Tat-SF1 are recruited to phosphorylated DSIF to facilitate productive elongation. NELF phosphorylation leads to its release and an increase of RNAPII clearance from the 5′LTR promoter. The SEC subunit ELL2 synergizes with Tat/P-TEFb to promote transcription elongation by preventing RNAPII backtracking. 6) RNAPII-mediated transcription elongation. The SEC/Tat/P-TEFb complex might stay associated to the elongating RNAPII. SL = stem-loop; P = phosphor; Ac = acetyl; T = Thr; Y = Tyr; S = Ser. Green arrow = acetylation; Red arrow = phosphorylation; Orange arrow = dephosphorylation; Blue arrow = ELL2 action on RNAPII.
