Figure 1. DISC1 765–835 interαcts with Ndel1/Nde1 CT-CC with high αffinity.
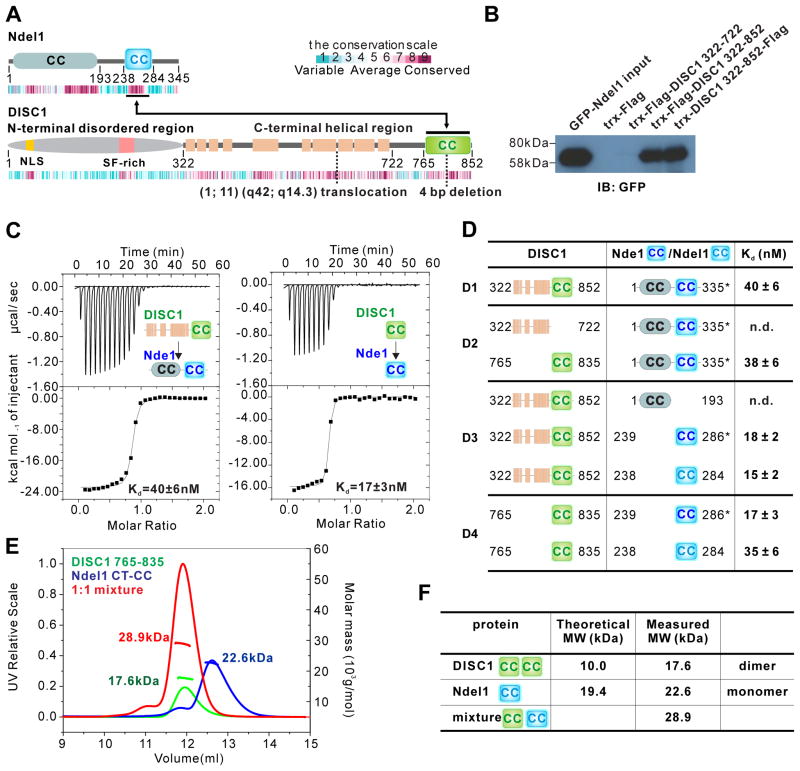
(A) Schematic diagram showing the domain organization of Ndel1 and DISC1. The beige-colored rectangles in DISC1 represent predicted α-helices. The two-way arrowed line shows the corresponding regions in the two proteins responsible for their specific interaction. The heat map below each scheme shows the amino acid sequence conservation of each protein throughout the evolution. The relationship between color and conservation is indicated at the upper right corner. CC, predicted coiled-coil region. Positions of translocation break point t(1;11)(q42;q14.3) found in a Scottish family and 4 bp deletion found in American schizophrenia family are highlighted.
(B) Pull-down assay showing the interaction between DISC1 C-terminal helical region (322–852) and full-length Ndel1. Purified DISC1 322–722 or 322–852 with trx and Flag tags were immunoprecipitated with cell lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with the full-length GFP-Ndel1 by anti-Flag beads, and the resulting immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for GFP-Ndel1.
(C) ITC-based measurements quantifying the binding affinities between DISC1 322–852 and full-length Nde1 (left panel) and DISC1 765–835 and Nde1 CT-CC (right panel). ITC, Isothermal Titration Calorimetry.
(D) ITC-based measurement summarizing the binding affinities between various DISC1 proteins and Nde1/Ndel1 proteins. The mapping results show that DISC1 765–835 and Nde1/Ndel1 CT-CC are the minimal binding regions for these two proteins to interact with high affinity. Nde1 CT-CC is labelled in dark blue, Ndel1 CT-CC in light blue. Due to its superior quality, we used full-length Nde1 indicated by an asterisk (*) when characterizing its interaction with DISC1. n.d., not detected.
(E and F) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis coupled with static light scattering analysis of DISC1 765–835 (green line), trx-Ndel1 CT-CC (blue line) and DISC1 765–835/trx-Ndel1 CT-CC complex (red line). The theoretical and measured molecular weights are listed in (F). The results indicate that DISC1 765–835 and Ndel1 CT-CC form a stable 1:1 complex in solution.
See also Figure S1 and S2.