Fig. 1.
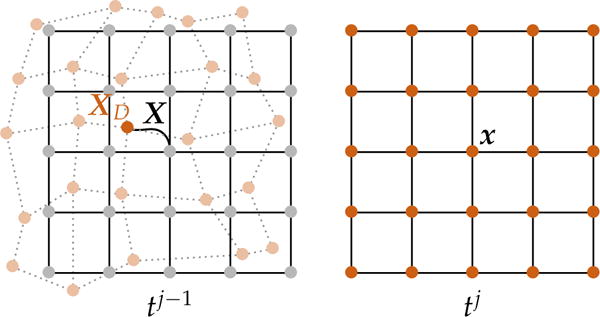
Tracing the characteristic X in a semi-Lagrangian scheme. We start with a regular grid Ωh (dark orange points on the right) consisting of coordinates x at time point tj. We assume we have already computed the intermediate solution uh of a given transport equation at time point tj−1; we know the input data on the regular grid at time point tj−1 (the regular grid nodes are illustrated in light gray). In a first step, we trace back the characteristic X by solving (14) backward in time subject to the initial condition X(t = tj) = x. Once we have found the characteristic (black line in the figure on the left) we can—in a second step—assign the value of uh at tj given at the departure point XD (dark orange point on the left) to x at tj based on some interpolation model. We illustrate the grid of departure points in light orange and the original grid in gray (left figure).
