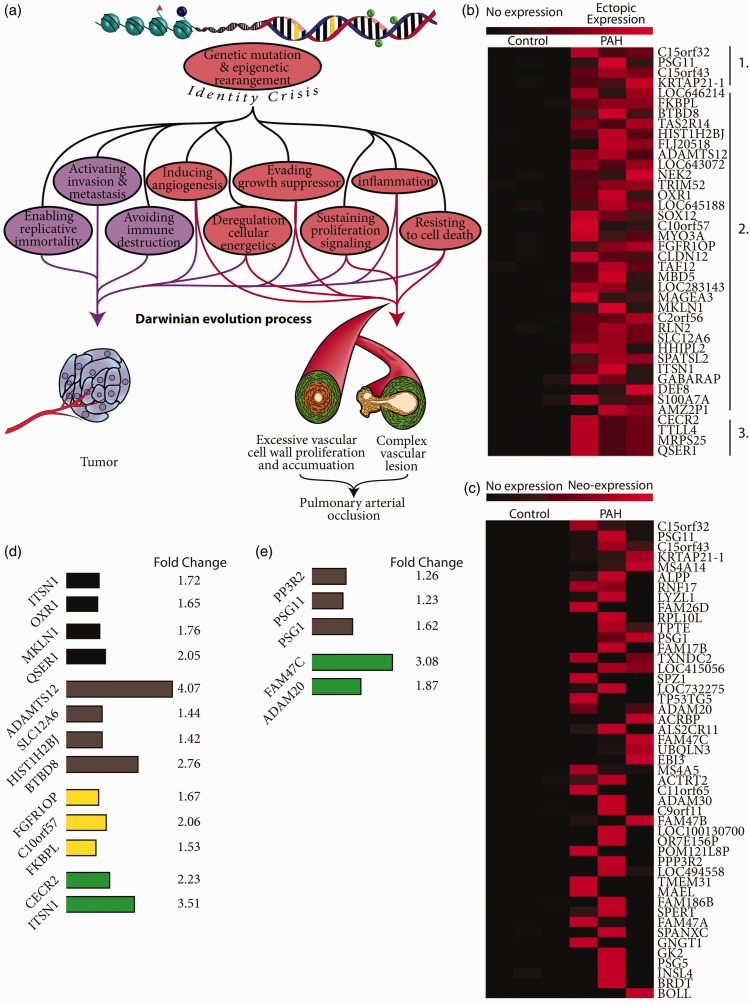
Fig. 1.
(a) Proposed model of identity crisis leading to PAH pathogenesis by a Darwinian evolution process. Genetic mutation and epigenetic rearrangement lead to aberrant gene expression and identity crisis development. In turn, identity crisis by a Darwinian evolution process gives rise to cancer cells hallmark acquisition and tumor development. In PAH, the same evolutionary process, with different selective pressure, would lead to PAH cancer hallmark acquisition, pulmonary arteries obstruction, and complex intimal lesions. (b) Ectopic expression of highly specific germline, placental, and embryonic genes in PAH lung. Ectopic expression heat map showing the ectopic expression in all human PAH lungs of highly specific germline, placental, and embryonic stem cell genes and their lack of expression in control lungs. Heat map has been divided into three groups: (1) placental and testis restricted expression; (2) germline cells predominant expression; (3) embryonic stem cells predominant expression (c) neo-expression of testis and placental restricted genes in PAH lung. Heat map illustrating the neo-expression in human PAH lungs of testis and placenta restricted genes and their absence of expression in control lungs. (d, e) Highly specific and restricted genes expression in previously performed microarray. (d) Aberrant expression of the same highly specific germline, placental and embryonic stem cell genes and (e) the neo-expression in human PAH lungs of testis and placenta restricted genes from microarray expression data of experiments previously performed in human PAH.17 These microarray expression analyses were performed on 12 lungs from end-stage PAH vs. 11 control patients (GSE 53408) (black); two primary isolated smooth muscle cells of PAH patients vs. two primary isolated control smooth muscle cells (GSE 21284) (gray); lungs from eight PAH patients associated with pulmonary fibrosis vs. 13 controls (GSE 15197) (yellow); lung from 18 PAH patients vs. 13 controls (GSE 15197) (green).