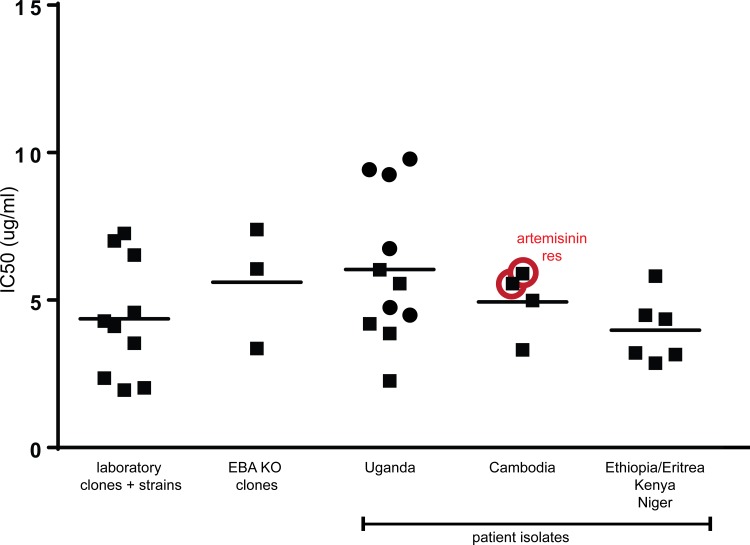
Fig 6. Sevuparin inhibits merozoite invasion of P. falciparum clones, strains and fresh isolates in vitro at low concentrations, independently of parasite origin or phenotype.
The invasion blocking capacity of sevuparin in 34 in vitro propagated P. falciparum isolates expressed as IC50. The inhibitory capacity of sevuparin was titrated in double dilution steps between 0.125 μg/mL and 1 mg sevuparin/mL culture. Ten laboratory isolates were either sensitive (3D7, 3D7PG12, Dd2, HB3) or resistant (R29, TM180, TM284, F32, 7G8, FCR3S1.2) to chloroquine. Three parasites of the W2mef background carried disrupted genes for EBA 140, EBA 175 or EBA 181 (EBA-KO). W2mef is a cloned line of parasites derived from the Indochina III-CDC strain. Of the fresh primary isolates 11 were from Ugandan children with either severe (dot) or uncomplicated (square) malaria and six isolates were from adults infected in Ethiopia/Eritrea, Kenya or Niger. Four Cambodian isolates were sensitive or resistant to artemisinin (red-circled square; IPC-4884, Pursut, artemisinin resistant (RSA 0-3h: 6,5%) and IPC 4912 artemisinin resistant (red circled square; RSA 0–3 h: 49%). ICP 5188 Rattanakiri and IPC 3663 Pailin were artemisinin sensitive (square).