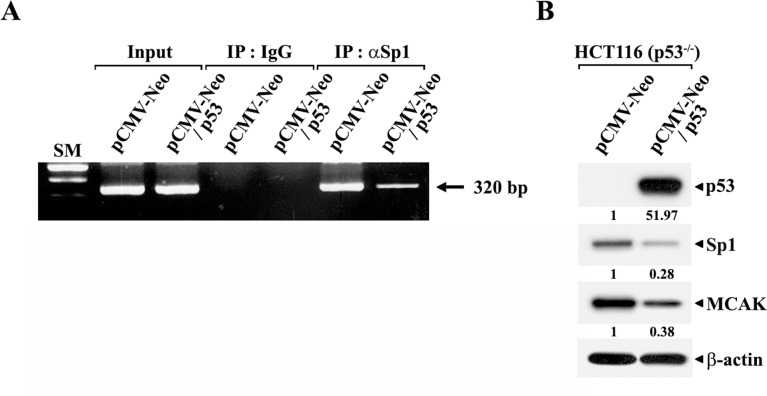
Fig 4.
ChIP analyses to detect the suppressive effect of p53 overexpression on the in vivo association of Sp1 with the MCAK promoter (A) and western blot analyses of individual protein levels in HCT116 (p53−/−) cells (B). The cells were transiently transfected with wild-type p53-expression vector (pCMV-Neo/p53) or empty-vector (pCMV-Neo). ChIP assays were performed using a ChIP Assay Kit. Formaldehyde-cross-linked chromatin was prepared from the cells and then immunoprecipitated with anti-Sp1 antibody or normal mouse IgG. The recovered immunoprecipitates were analyzed by PCR with specific primers to amplify the 320-bp MCAK promoter region (−266/+54) possessing two p53-REs (p53-RE1 at −173/−166 and p53-RE2 at −245/−238) as well as two GC-motifs (GC1 at −93/−84 and GC2 at −119/−110) using the SacI-forward primer (5'-AGGA-GCTCAGTCAAGTTTCTAATCTG-3') and the BglII-reverse primer-2 (5’-AGAGATCTCGGAGA-GTCAGCAAGGAAGAG-3’). The 320-bp PCR products were resolved on a 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and are indicated by arrows. Western blot analyses were performed as described in Materials and methods. A representative study is shown and two additional experiments yielded similar results.