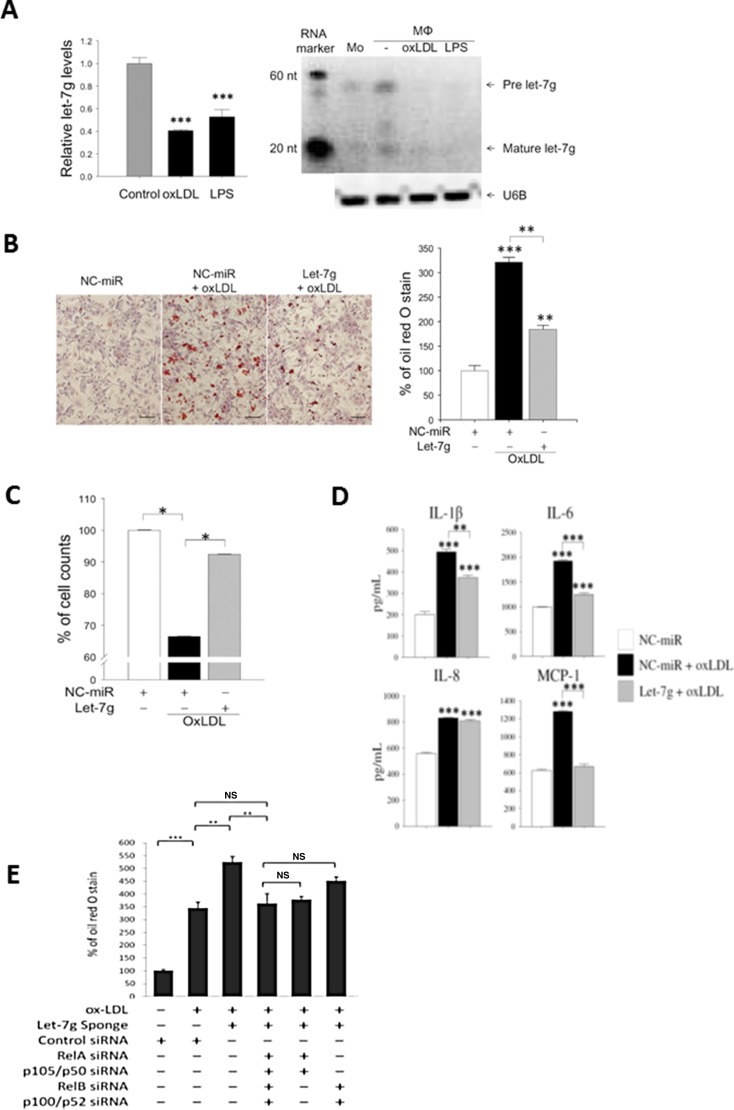
Figure 1. Let-7g reduces foam cell formation, increases macrophage viability and decreases inflammation.
Macrophages were differentiated from THP-1 cells. (A) let-7g RNA expression levels in macrophages treated with oxLDL (40 μg/ml) or LPS (100 ng/ml), respectively, for 24 hours. (B) Macrophages were transfected with let-7g mimic (50 nmol/L) for 24h, and then stained with oil red O (ORO). Scale bar, 100 μm. The quantified data were shown in the bar chart. (C) Cell viability was determined by trypan blue stain at 24 h after microRNA transfection. (D) Cytokine and chemokine in the culture medium of let-7g-transfected and oxLDL-treated macrophages. The data were measured by ELISA. (E) Knockdown of let-7g by LV-let-7g-sponge caused a significant increase of lipid accumulation, but the effect was reversed by inhibiting canonical signaling (5th bar), non-canonical signaling (6th bar) or both signaling pathways (4th bar) by siRNAs for NF-κB transcription factors. The data were from at least three independent experiments. Data in each bar chart are presented as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.