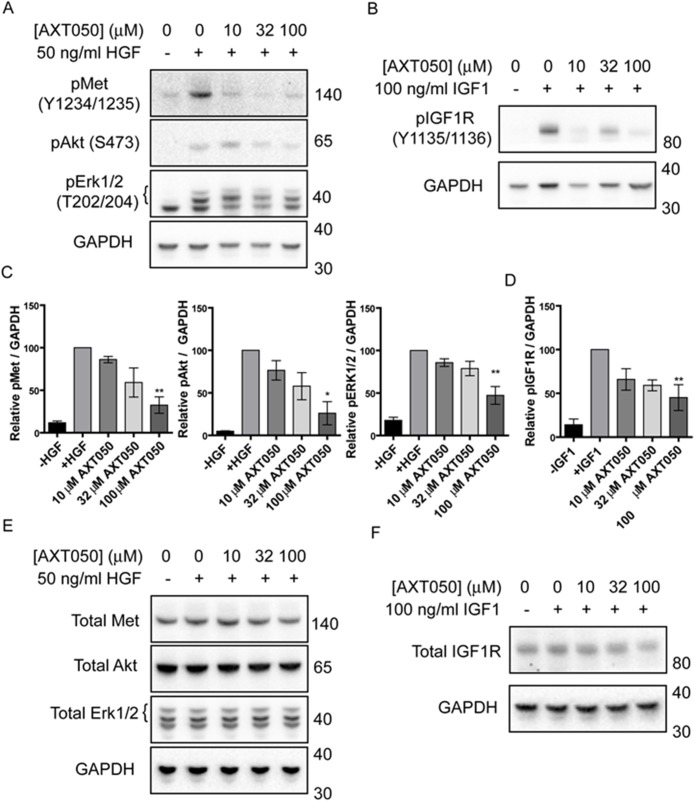
Figure 2. AXT050 inhibits IGF1R and c-Met signaling in HCC cells.
(A) Western blotting demonstrating dysregulation of HGF mediated pMet, pAkt and pErk signaling pathways following treatment of HepG2 cells with AXT050. The presented figures were cropped from images of the original membranes that were cut at approximately 70-75 kDa. The top portion was blotted for pMet and the bottom portion blotted sequentially for GAPDH, pAkt, and pErk 1/2 in that order. Bands for GAPDH are still visible in the pErk 1/2 image (lowest bands) because of this sequential blotting technique. (B) Western blotting showing dysregulation of IGF1 mediated IGF1R signaling following treatment of HepG2 cells with AXT050. The presented figures were cropped from images of the original membranes that were cut at approximately 70-75 kDa. The top portion was blotted for pIGF1R and the bottom portion blotted for GAPDH. (C, D) Semi-quantitative assessment of band intensity of signals of activated pMet, pAkt, pErk and pIGF1R normalized to GAPDH showing significant downregulation of Met and IGF1R signaling with increasing concentrations of AXT050 (10 μM, 32 μM and 100 μM). Data presented as mean ± SEM (N=3); pMet (p = 0.0009), pAkt (p = 0.0029), pERK 1/2 (p = 0.0002), and pIGF1R (p = 0.0002) by 1-way ANOVA. * and ** designate significant (< 0.05) and highly significant (<0.01) differences respectively by Tukey test compared to the growth factor, 0 μM AXT050 treated samples. (E, F) Representative western blots showing total protein levels of Met, AKT, ERK 1/2 (E) and IGF1R (F) in HepG2 lysates following treatment with AXT050. GAPDH is provided as a loading control. Blots were otherwise prepared as described for phosphorylated equivalents (A and B).