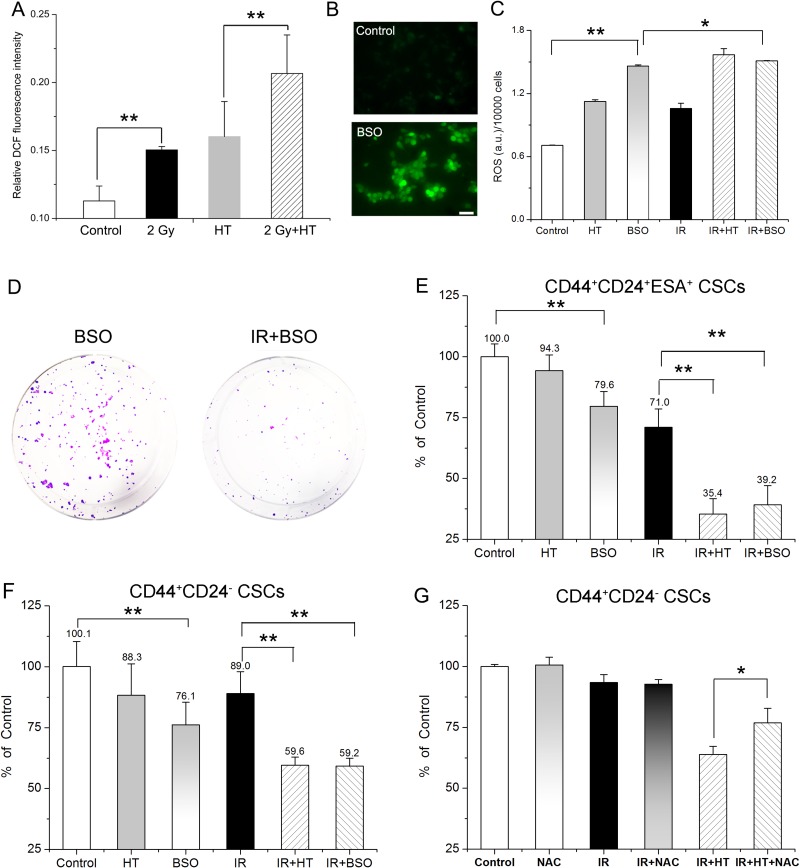
Figure 5. Association of elevated ROS level with HT induced radiosensitization in breast CSCs and pancreatic CSCs.
(A) Intracellular ROS concentrations of CD44+CD24- CSCs in control, HT, 2 Gy and 2 Gy+HT treatment groups. No treated group as control. (B) Representative images of intracellular ROS concentrations in CD44+CD24– CSCs treated with or without 1 mM BSO for 24 hours. Bar = 50 μm. (C) Intracellular ROS concentrations of CD44+CD24– CSCs in the indicated treatment groups. (D) Representative images of colony formation in CD44+CD24+ESA+ CSCs at 14 days after treated with BSO (1 mM) or IR+BSO. (E) Colony survival of CD44+CD24+ESA+ CSCs treated with or without 1 mM BSO for 24 hours prior to the indicated treatments. Each data was normalized to that of the sham-treated control. (F) CD44+CD24– CSCs were cultured as mammospheres with or without 1 mM BSO for 24 hours prior to the indicated treatments. Mammosphere survival of each group was analyzed statistically. Each data was normalized to that of the sham-treated control. (G) CD44+CD24– CSCs after indicated treatments were cultured as mammospheres in presence or absence with 100 μM NAC. Post 7 days’ culturing, number of mammospheres per 2500 cells were counted and mammosphere survival of each group was analyzed statistically. Each data was normalized to that of the sham-treated control. The results are presented as the mean ± SD, as determined from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.